Phase behavior of nanostruturated membranes based on PVA, CS, H3PO2, and Nb2O5
Comportamiento de fases de membranas nanoestruturadas basadas en PVA, CS, H3PO2 y Nb2O5

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright statement
The authors exclusively assign to the Universidad EIA, with the power to assign to third parties, all the exploitation rights that derive from the works that are accepted for publication in the Revista EIA, as well as in any product derived from it and, in in particular, those of reproduction, distribution, public communication (including interactive making available) and transformation (including adaptation, modification and, where appropriate, translation), for all types of exploitation (by way of example and not limitation : in paper, electronic, online, computer or audiovisual format, as well as in any other format, even for promotional or advertising purposes and / or for the production of derivative products), for a worldwide territorial scope and for the entire duration of the rights provided for in the current published text of the Intellectual Property Law. This assignment will be made by the authors without the right to any type of remuneration or compensation.
Consequently, the author may not publish or disseminate the works that are selected for publication in the Revista EIA, neither totally nor partially, nor authorize their publication to third parties, without the prior express authorization, requested and granted in writing, from the Univeridad EIA.
Show authors biography
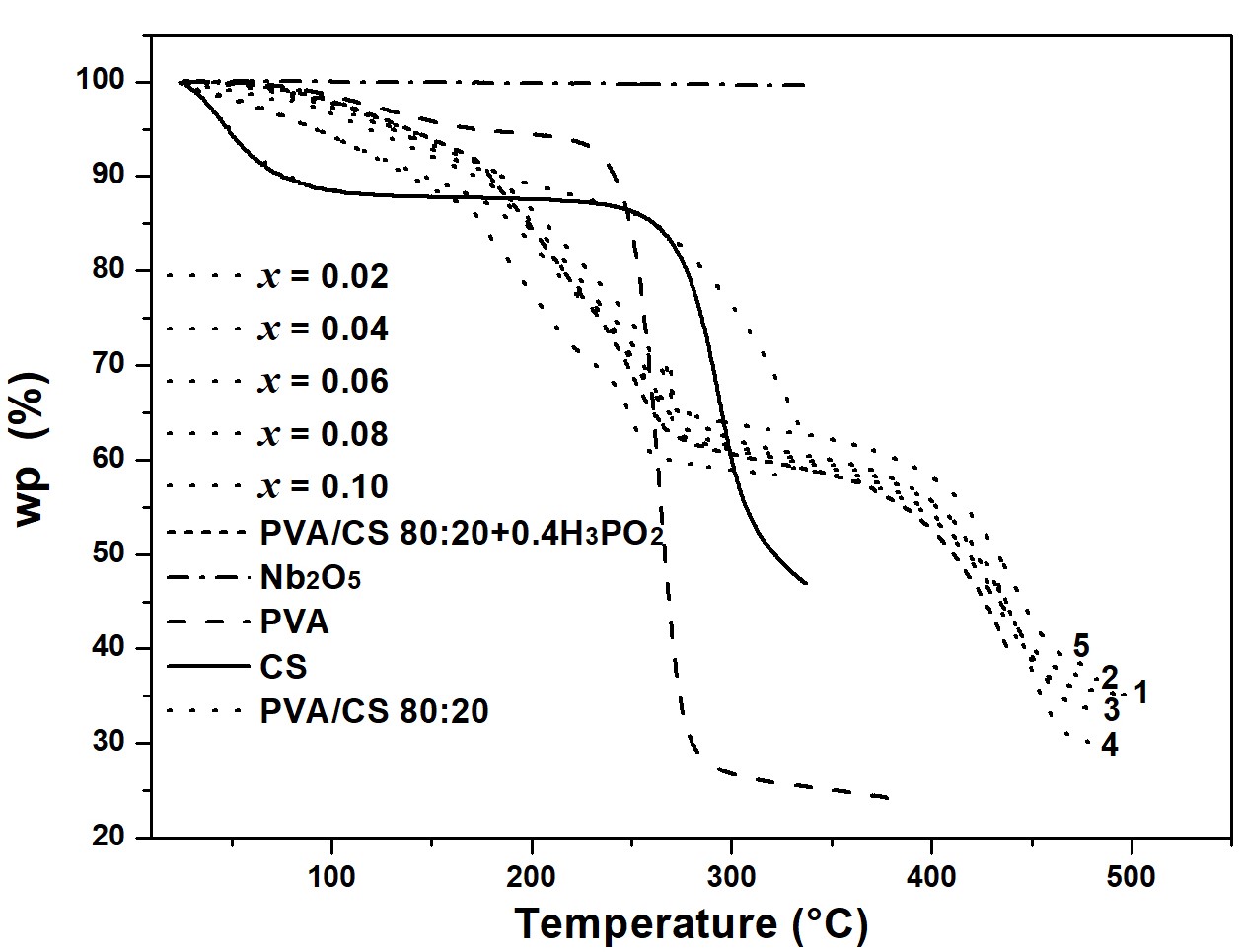
Thermal behavior (phase equilibria) of nanostructured membranes based on poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), chitosan (CS), hypophosphorous acid (H3PO2), nanoporous micro-particles of niobium oxide (Nb2O5) using Differential Scanning Calorimetric (DSC) and Thermogravimetry Analysis (TGA) techniques were studied. Membranes PVA-CS 80:20+40%H3PO2+xNb2O5 with between x=0.02 and x=0.10 were prepared. For the DSC thermograms, the glass transition of PVA/CS 80:20 was observed at Tg~26°C, for PVA/CS 80:20+40%H3PO2 at 95°C, and for those doped with Nb2O5 at 110°C. The melting point of PVA y PVA/CS 80:20 membranes was around 210°C, for PVA/CS 80:20+40%H3PO2 is no clearly observed, indicating the dominance of their amorphous phase. For doped with Nb2O5, the melting of their crystalline phases was around 180°C. Above 430°C, all membranes break down. The TGA thermograms for all membranes showed a continuous weight loss as the temperature increased to 200°C, this loss is due to the absorbed water molecules at the membrane’s surface or caught inside of the polymer chains. Above 200°C, the membranes loss weight more quickly, being higher for the membranes without doping with Nb2O5, is observed.
Article visits 436 | PDF visits 260
Downloads
- Ahn, J., Wang, G.X., Liu, H., and Dou, S., 2003. Nanoparticle-dispersed PEO polymer electrolytes for Li batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 119–121, pp. 422–426. doi: 10.1016/S0378-7753(03)00264-7.
- Casciola, M., Alberti, G., Ciarletta, A., Cruccolini, A., Piaggio, P., and Picaa, M., 2005. Nanocomposite membranes made of zirconium phosphate sulfophenylenphosphonate dispersed in polyvinylidene fluoride: Preparation and proton conductivity. Solid State Ionics, 176(39), pp. 2985–2989. doi: 10.1016/j.ssi.2005.09.036
- González, Y.F. y Vargas, R.A., 2011. Estudio de las propiedades termodinámicas y eléctricas de materiales compuestos póliméricos basados en el poli(vinil alcohol) (PVA) + H3PO2 + TiO2. Revista Iberoamericana de Polímeros, 12(2), pp. 64–75.
- Ma, B., Qin, A., Li, X., Zhao, X., and He, C., 2014. Structure and properties of chitin whisker reinforced chitosan membranes. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 64, pp. 341–346. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.12.015.
- Mena, D.F., 2014. Caracterización de fases conductoras iónicas en membranas basadas con quitosano y polivinil alcohol. Trabajo de grado, Universidad del Valle.
- Steele, B.C.H. and Heinzel, A., 2001. Materials for fuel-cell technologies. Nature, 414, pp. 345–352. doi: 10.1038/35104620.
- Vargas, R.A., Garcia, A., and Vargas, M.A., 1998. Phase behavior of complexes of PVA and acid salts. Electrochimica Acta, 43(10-11), pp. 1271–1274. doi: 10.1016/S0013-4686(97)10029-9.
- Wang, X.L., Fan, L.Z., Xu, Z.H., Lin, Y.H., and Nan, C.W., 2008. Temperature dependent ionic transport properties in composite solid polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics, 179(27), pp. 1310–1313. doi: 10.1016/j.ssi.2008.01.045.
- Yuan, H.K., Ren, J., Ma, X.H., and Xu, Z.L., 2011. Dehydration of ethyl acetate aqueous solutions by pervaporation using PVA/PAN hollow fiber composite membrane. Desalination, 280(1-3), pp. 252–258. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2011.07.002.




