Geometric Effects on the Electronic and Optical Properties of GaN Conical Quantum Dots
Efectos geométricos sobre las propiedades electrónicas y ópticas de puntos cuánticos cónicos de GaN (Punto cuántico cónico)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright statement
The authors exclusively assign to the Universidad EIA, with the power to assign to third parties, all the exploitation rights that derive from the works that are accepted for publication in the Revista EIA, as well as in any product derived from it and, in in particular, those of reproduction, distribution, public communication (including interactive making available) and transformation (including adaptation, modification and, where appropriate, translation), for all types of exploitation (by way of example and not limitation : in paper, electronic, online, computer or audiovisual format, as well as in any other format, even for promotional or advertising purposes and / or for the production of derivative products), for a worldwide territorial scope and for the entire duration of the rights provided for in the current published text of the Intellectual Property Law. This assignment will be made by the authors without the right to any type of remuneration or compensation.
Consequently, the author may not publish or disseminate the works that are selected for publication in the Revista EIA, neither totally nor partially, nor authorize their publication to third parties, without the prior express authorization, requested and granted in writing, from the Univeridad EIA.
Show authors biography
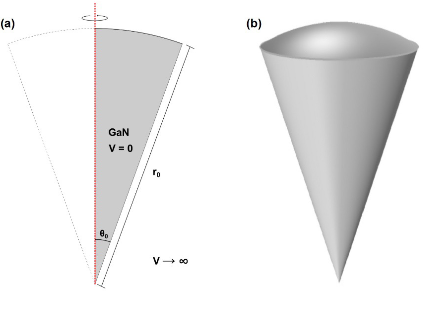
Using the effective mass approximation and finite element method numerical calculations, optical, and electronic properties of an electron confined in a GaN quantum dot are reported for a spherical conical sector. Electronic states, the square of the dipole moment, optical absorption coefficients, and changes in the refractive index are reported as functions of the radius and the apical angle of the structure. From the study it can be concluded that: i) suitable choices of the apical angle and the radius of the quantum dot can give rise to magnifications in the optical properties and ii) redshifts of the resonant structures of the optical properties are clearly associated with the increase in both the apical angle and the radius of the structure.
Article visits 578 | PDF visits 311
Downloads
- Avazzadeh, Z.; Bahramiyan, H.; Khordad, R.; Mohammadi, S. A. (2016). Diamagnetic Susceptibility of an Off-Center Hydrogenic Donor in Pyramid-Like and Cone-Like Quantum Dots. Eur. Phys. J. Plus, 131(121) Abril, pp. 1-8. [Online] Disponible en: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2016-16121-8. [Consultado 11 de mayo de 2020].
- Çakır, B.; Yakar, Y.; Özmen, A. (2012). Refractive Index Changes and Absorption Coefficients in a Spherical Quantum Dot with Parabolic Potential. J. Lumin., 132(10) Octubre, pp. 2659-2664. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2012.03.065
- COMSOL Multiphysics, v. 5.4. COMSOL AB, Stockholm, Sweden.
- Dezhkam, M.; Zakery, A. (2012). Exact Investigation of the Electronic Structure and the Linear and Nonlinear Optical Properties of Conical Quantum Dots. Chin. Opt. Lett., 10(12) Diciembre, pp.1-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.3788/COL201210.121901
- Gil-Corrales, A.; Morales, A. L.; Restrepo, R. L.; Mora-Ramos, M. E.; Duque, C. A. (2017). Donor-Impurity-Related Optical Response and Electron Raman Scattering in GaAs Cone-Like Quantum Dots. Physica B, 507 Febrero, pp. 76-83. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2016.11.033
- Hiruma, K.; Haraguchi, K.; Yazawa, M.; Madokoro, Y.; Katsuyama, T. (2006). Nanometre-Sized GaAs Wires Grown by Organo-Metallic Vapour-Phase Epitaxy. Nanotechnology, 17(11) Mayo, pp. S369–S375. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/17/11/S23
- Iqraoun, E.; Sali, A.; Rezzouk, A.; Feddi, E.; Dujardin, F.; Mora-Ramos, M. E; Duque, C. A. (2017). Donor Impurity-Related Photoionization Cross Section in GaAs Cone-Like Quantum Dots Under Applied Electric Field. Philosophical Magazine, 97(18) Marzo, pp. 1445-1463. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/14786435.2017.1302613
- Kanyinda-Malu, C.; Cruz, M. R. (2003). Interface Phonon Modes in Truncated Conical Self-Assembled Quantum Dots. Surf. Sci., 529(3) Abril, pp. 503-514. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-6028(03)00335-2
- Khordada, R.; Bahramiyanb, H. (2014). Optical Properties of a GaAs Cone-Like Quantum Dot: Second and Third-Harmonic Generation. Opt. Spectrosc., 117(3) Septiembre, pp. 447–452. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0030400X14080165
- Lelong, Ph.; Bastard, G. (1996). Binding Energies of Excitons and Charged Excitons in GaAsGa(In)As Quantum Dots. Solid State Commun, 98(9) Junio, pp. 819-823. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-1098(96)00024-5
- Li, Y.; Voskoboynikov, O.; Lee, C. P.; Sze, S. M.; Tretyak, O. (2001). Electron Energy State Dependence on the Shape and Size of Semiconductor Quantum Dots. J. Appl. Phys., 90(12) Diciembre, pp. 6416-6420. http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1412578
- Ngo, C. Y.; Yoon, S. F.; Fan, W. J.; Chua, S. J. (2006). Effects of Size and Shape on Electronic States of Quantum Dots. Phys. Rev. B, 74(24) Diciembre, pp. 1-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.74.245331
- Nguyen, C. V.; Hieu, N. N.; Duque, C. A.; Poklonski, N. A.; Ilyasov, V. V.; Hieu, N. V.; Dinh, L.; Quang, Q. K.; Tung, L. V.; Phuc, H. V. (2017). Linear and Nonlinear Magneto-Optical Absorption Coefficients and Refractive Index Changes in Graphene. Opt. Mater., 69 Julio, pp. 328-332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2017.04.053
- Niculescu, E.; Tiriba, G.; Spandonide, A. (2015). Optical Absorption in Pyramid-Shaped Quantum Dots Under Applied Electric and Magnetic Fields. U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, 77(3) Enero, pp. 229-240.
- Rezaei, G.; Karimi, M.J.; Pakarzadeh, H. (2013). Magnetic Field Effects on the Electron Raman Scattering in Coaxial Cylindrical Quantum Well Wires. J. Lumin., 143 Noviembre, pp. 551-557. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2013.05.039




