Assessment of the sustainability of the high-frequency localized irrigation system of the ASOLABELLA- irrigation mini-district, Pereira Municipality.
Valoración de la sostenibilidad del sistema de riego localizado de alta frecuencia del minidistrito de riego ASOLABELLA, Municipio de Pereira

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright statement
The authors exclusively assign to the Universidad EIA, with the power to assign to third parties, all the exploitation rights that derive from the works that are accepted for publication in the Revista EIA, as well as in any product derived from it and, in in particular, those of reproduction, distribution, public communication (including interactive making available) and transformation (including adaptation, modification and, where appropriate, translation), for all types of exploitation (by way of example and not limitation : in paper, electronic, online, computer or audiovisual format, as well as in any other format, even for promotional or advertising purposes and / or for the production of derivative products), for a worldwide territorial scope and for the entire duration of the rights provided for in the current published text of the Intellectual Property Law. This assignment will be made by the authors without the right to any type of remuneration or compensation.
Consequently, the author may not publish or disseminate the works that are selected for publication in the Revista EIA, neither totally nor partially, nor authorize their publication to third parties, without the prior express authorization, requested and granted in writing, from the Univeridad EIA.
Show authors biography
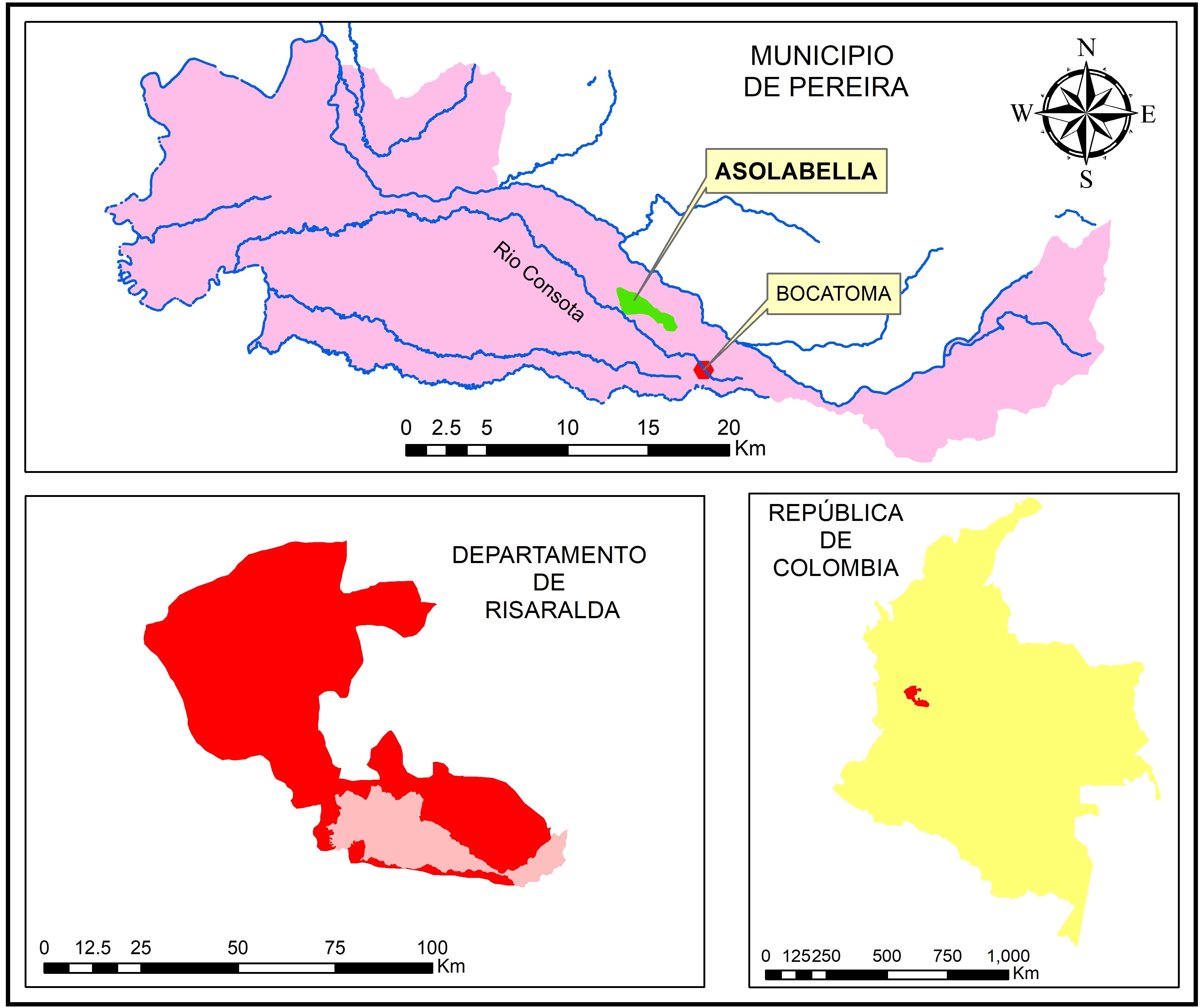
In this study, sustainability factors were assessed in the La Bella mini-irrigation district in the municipality of Pereira-Colombia that uses the high-frequency localized irrigation method (RLAF). The study was based on the identification and evaluation of factors and indicators that affect sustainability in RLAF systems on a real scale. The assessment of sustainability factors was carried out by means of a multi-criteria analysis (AHP) and the statistical process of grouping intervals that allowed defining five levels of sustainability assessment of each property after the multi-criteria analysis. The results show that the factors that contribute most to the sustainability of the systems that use RLAF are profitability and water quality. Limiting factors for sustainability were the availability of water and the operation of the RLAF system, due to the conflict between supply and demand in dry seasons and the lack of technical knowledge to establish the operating rules for the application of flows and to follow a RLAF systems operation and maintenance guide. The study allowed estimating a moderate level of sustainability for ASOLABELLA RLAF systems.
Article visits 763 | PDF visits 451
Downloads
- Elgilany A., Faki H. y Elobeid H (2007). Assessment of on farm water use efficiency in the public irrigated schemes in the river nile state of sudan. Paper presented at the International Agricultural Research for Development, 9–11 October:Witzenhavsen, Germany. doi: 10.1080 / 19443994.2013.808785
- ASOLABELLA, (2016). Informe Técnico. Programa de Uso Eficiente y Ahorro del Agua. Convenio interadministrativo. No. 402 – 16 de 2016.
- ASAE EP405.1. (2003). Engineering Practice EP405.1, FEB03, Desing and Installation of Microirrigation Systems. ASAE, St. Joseph, Michigan. Pp 901-905.
- Bojórquez, F. (2008). Parámetros de agua de riego. Productores de Hortalizas. Available at: http://www.hortalizas.com/irrigacion/parametros-de-agua-de-riego/. (Accessed: el 2 de julio de 2020).
- CAF (Banco de Desarrollo de América Latina), (2013). La irrigación eficiente fortalece la agricultura ecológica. [En línea]. Available at: https://www.caf.com/es/actualidad/noticias/2013/10/la-irrigacion-eficiente-fortalece-la-agricultura-ecologica/?parent=26408. (Accessed: 13 de junio de 2019).
- Charles, M y P, Burt. (2002). Riego por goteo y por micro aspersión para árboles, vides y cultivos anuales, Vida Rural, 1: 744-760.
- Daza, M., Reyes-Trujillo, A., Loaiza-Cerón, W., y Fajardo-Vásquez, M.P. (2012) Índice de sostenibilidad del recurso hídrico agrícola para la definición de estrategias sostenibles y competitivas en la Microcuenca Centella Dagua – Valle del Cauca. Gest. Ambient., Volumen 15, Número 2, p. 47-58. Doi:10.15446/ga
- Euderink J., Vollaers V y Wesseling (2017). Informe Tecnico. Problems Obstructing Efficient Water Use In Colombia. Delf
- FAO, (2005). Uso del agua en la agricultura. Enfoques. Available at; http://www.fao.org/ag/esp/revista/0511sp2.htm. (Accessed: el 3 de junio de 2017).
- FAO, (2008). El desarrollo del microrriego en américa central. Oportunidades, Limitaciones y Desafíos Cap. IV Factores que se deben considerar para seleccionar el sistema de riego más adecuado. Available at: http://www.fao.org/3/a-aj470s.pdf. (Accessed: el 4 de junio de 2018).
- Falconi, F y Burbano R. (2004). Instrumentos económicos para la gestión ambiental: decisiones monocriteriales versus decisiones multicriteriales. Revista Iberoamericana de Economía Ecológica. Vol. 1: 11-20
- Fernández, G; Gómez, G y López, J. (2010). Análisis de la sostenibilidad agraria mediante indicadores sintéticos. Sociedad Brasilera de economía, administración y economía rural. Tesis (Doctoral). Available at: https://issuu.com/toribioroman/docs/analis.ds.indic.sinteticos. (Accessed el 22 de octubre de 2018).
- Figueira, J., Greco, S. and Ehrgott, M. (2005) ‘Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis, State of the Art Surveys’, Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis: State of the Art Surveys, 78. doi: 10.1007/b100605.
- García C, baucells P, Pérez Leira R, Rodés R. (2003). Organización: Aspecto Clave en la Sostenibilidad de los Sistemas de Riego y en la Eficiencia del Uso del Agua. Rev Ciencias Técnicas Agropecuarias;12. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303381703. (Accessed el 3 de Julio de 2018).
- Gomez-Limon J, Sanchez-Fernandez G.(2009). Empirical evaluation of agricultural sustainability using composite indicators. Ecol Econ. 2010;69:1062-1075. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2009.11.027
- H. Ibrahim S. Sustainability Assessment and Identification of Determinants in Community-Based Water Supply Projects using Partial Least Squares Path Model. J Sustain Dev Energy, Water Environ Syst. 2017;5:345-358. doi:10.13044/j.sdewes.d5.0153
- Instituto de Hidrología, Meteorología y Estudios Ambientales [IDEAM], (2014). Estudio Nacional del Agua 2014. 496 páginas Bogotá, D. C. Available at: http://www.andi.com.co/Uploads/ENA_2014.pdf. (Accessed el 25 de agosto de 2018).
- Latorre J; Sánchez L; Fernández J; Rojas J; Bastidas S y Vargas S, (2003). Análisis de la sostenibilidad en sistemas de agua y saneamiento. 43 proyectos en la zona rural de Nicaragua. IRC-Cinara.
- López, Hernández, Pérez y Gonzales, (1992). Riego localizado, ediciones Multi-Prensa, pp 19-37.
- Ministry of Agriculture and Foresty New Zealand (MAF) (1997). Indicators of sustainable irrigated agriculture. Technical Paper No. 00/03: Manukau, New Zealand.
- Márquez G, (2000). Vegetación, población y huella ecológico como indicadores de sostenibilidad en Colombia. Gestión y ambiente 5. Universidad nacional de Colombia. Available at: http://www.idea.unal.edu.co/publica/docs/veg-pob-huella-eco.pdf. (Accessed el 13 de agosto de 2018).
- Masera, O. y López-Riadura. (2000). El Marco MESMIS. En Sustentabilidad y Sistema Campesinos. México, D. F: Mundiprensa
- Millar, A. (1993). Ambiente y sostenibilidad de la agricultura bajo riego en Brasil. Instituto iberoamericano de cooperación para la agricultura. Programa de generación y transferencia de tecnología. Serie de documentos IICA. No. 37. P.77. San José, CR:
- Nakayama F y Bucks, D. (1986). Trickle irrigation for crop production-Desing operation and managment. Edit. Elservier Science Publishers B. V. Amsterdam. 383 p.
- Noble, N. (2007). Practical answers technical information online. Micro-Irrigation. Available at: http://practicalaction.org/ practicalanswers/product_info.php?cPath=24_78&products_id=56. (Accessed el 13 de agosto de 2018).
- Pizarro, C. (1996). Riego localizado de alta frecuencia: Calidad de agua para riego. España: Ediciones Mundi–Prensa, 137 p.
- Ramírez-Jaramillo G., Cano-González A., Tun Dzul J., Sánchez-Cohen I y Lomas-Barrie C. (2007). Diagnóstico y evaluación de sistemas de riego en el minidistrito 048 Ticul, Yucatán Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Agrícolas. Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Agrícolas.2011.5-18. Available at: https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=263120987001. [Consultado el 2 de junio de 2018]. (Accessed el 19 de noviembre de 2019).
- Reche, (1993). Limpieza y mantenimiento de las instalaciones de riego por goteo. Hojas Divulgadoras Nro. 8-9/93 HD 63 pp. Available at https://www.mapama.gob.es/ministerio/pags/biblioteca/hojas/hd_1993_08-09.pdf. (Accessed el 12 de octubre de 2019).
- Saaty T.(2008). Decision making with the Analytic Hierarchy Process. Int J Serv Sci Int J Serv Sci. 2008;1:83-98. doi:10.1504/IJSSCI.2008.017590
- Salazar L, Saravia R, Rafael R. (2010). Sustentabilidad y Autogestión de Sistemas de Riego. Programa de Desarrollo Agropecuario Sustentable PROAGRO. Cochabamba. Bolivia. 67 pp. [En línea]. Available at: https://wocatpedia.net/images/temp/2/2f/20130121114029!phpjyLpiN.pdf. (Accessed el 13 de agosto de 2019).
- Santhi C., Pundarikanthan NV. (1996). Irrigation Scheduling in a Developing Country: Experiences from Tamil Nadu, India. Irrigation Scheduling: From Theory to Practice-Proceedings. Water Report 8. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy. Available at: http://www.fao.org/3/w4367e/w4367e17.htm. Consultado el 28 de noviembre de 2018. (Accessed el 18 de noviembre de 2019).
- Stockle CO, Papendick RI, Saxton KE, Campbell GS. (1994.) A framework for evaluating the sustainability of agricultural production system. American Journal of Alternative Agriculture 9(1&2): 45–51. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0889189300005555
- Tiewtoy S, Clemente R, Perret S, Babel M, Weesakul S. (2011). Irrigation sustainability assessment of selected projects in tha Chin Basin, Thailand. Irrig Drain. 2011;60:296-307. doi:10.1002/ird.583
- Vichi-Flores, (2013). Adopción de tecnología de riego para el uso sustentable del recurso hídrico en México. Trayectorias. 2013; 15 (36): 65-82.ISSN: 2007-1205. Available at. https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=607/60727448004. (Accessed el 15 de noviembre de 2019).
- Vermeiren, L. y Jobling, G. (1986). Riego localizado. Serie Riego y Drenaje, N° 36. Roma: FAO, 203 p.




