Design of an internet of things (IoT) system for blood pressure monitoring
Diseño de un sistema internet de las cosas (IoT) para el monitoreo de la presión arterial

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright statement
The authors exclusively assign to the Universidad EIA, with the power to assign to third parties, all the exploitation rights that derive from the works that are accepted for publication in the Revista EIA, as well as in any product derived from it and, in in particular, those of reproduction, distribution, public communication (including interactive making available) and transformation (including adaptation, modification and, where appropriate, translation), for all types of exploitation (by way of example and not limitation : in paper, electronic, online, computer or audiovisual format, as well as in any other format, even for promotional or advertising purposes and / or for the production of derivative products), for a worldwide territorial scope and for the entire duration of the rights provided for in the current published text of the Intellectual Property Law. This assignment will be made by the authors without the right to any type of remuneration or compensation.
Consequently, the author may not publish or disseminate the works that are selected for publication in the Revista EIA, neither totally nor partially, nor authorize their publication to third parties, without the prior express authorization, requested and granted in writing, from the Univeridad EIA.
Show authors biography
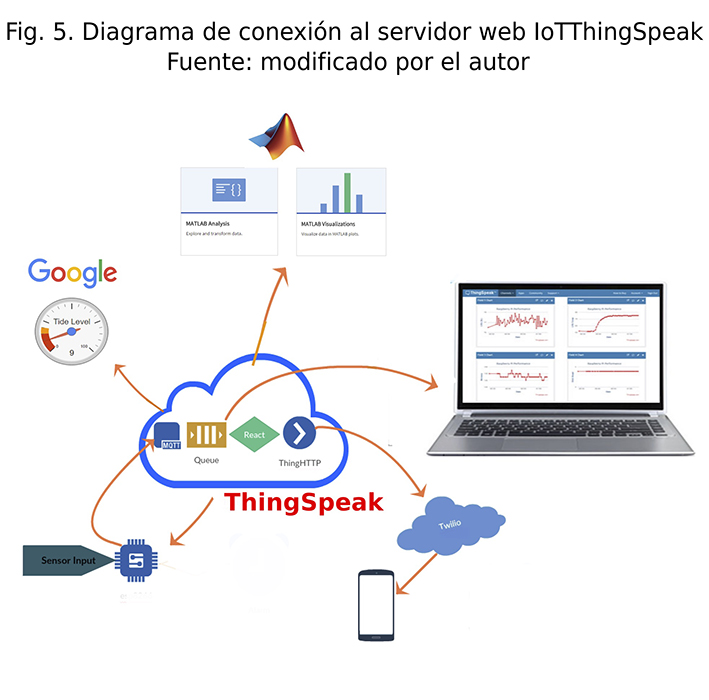
This article describes the design and building processes of an IoT biomedical equipment for monitoring the blood pressure of patients at their place of residence. The equipment, easy to operate, can be used directly by the patient after receiving a brief instruction from healthcare personnel. In this way, the states of agitation and stress that usually affect this physiological variable are reduced. In the prototype building, six design stages are incorporated, ranging from the electronic circuitry required for analog signal acquisition and conditioning, to the inter-connectivity of devices and data transfer to the cloud proposed by the IoT model. Validation tests and experiments suggest that the prototype has the potential to provide a solution to monitoring blood pressure at home, reducing the displacement of patients to hospital centers.
Article visits 1598 | PDF visits 856
Downloads
- Batista, O., Del Rey, R., Ramos, J., Ruso, R. (2001). Una implementación efectiva del método oscilométrico para la medición de la presión arterial. Memorias II Congreso Latinoamericano de Ingeniería Biomédica. La Habana, Cuba. https://docplayer.es/45718453-Una-implementacion-efectiva-del-metodo-oscilometrico-para-la-medicion-de-la-presion-arterial.html
- Bose, J., Das, K., Sahni, N. (2018). Web APIs for Internet of Things. Doi: 10.1109/ICACCI.2018.8554612
- Champaneria, T., Nakhuva, B. (2015). Study of varius Internet of things plataforms. International Journal of Computer Science & Engineering Survey (IJCSES) Vol.6, No.6
- Claus, T. (2016). APIs Para Dummies, Edicion limita IBM. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Cobos, A. (2016). Diseño e implementación de una arquitectura IoT basada en tecnologías Open Source. (Tesis en Master Universitario De Ingeniería De Telecomunicación), Departamento de Ingeniería Telemática, Escuela Técnica Superior De Ingeniería, Universidad de Sevilla, Sevilla.
- Core electronics. (2018). Startup with Onion omega 2. Retrieved from: https://core-electronics.com.au/tutorials/onion/onion-omega-2-how-to-run python-script-on-startup-boot.html
- Cuesta, A. (2004), Medición de la tensión arterial, errores más comunes. (Trabajo investigativo), Departament d’Infermeria, Universiat de Valéncia, Valencia.
- Fluke. (2019). BP Pump 2 NIBP Blood Pressure Simulator. https://www.flukebiomedical.com/products/biomedical-test-equipment/patient-monitor-simulators/bp-pump-2-nibp-blood-pressure-simulator
- Fundación BBVA. (2009). Libro de la salud cardiovascular del Hospital Clínico San Carlos y de la Fundación BBVA, 1.a edición. Bilbao, Editorial Nerea, S. A.
- Gómez, M., Ondelholf, D., Teernstra, L. (2014). ThingSpeak an API and Web Service for the Internet of Things. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/ThingSpeak-–-an-API-and-Web-Service-for-the-of-Maureira/5dcd7d5c5a6e30aa5fa3bc2fbcbf2caa5d2e0798#paper-header
- González, J. U., Olvera, D. J. (2013). Diseño y construcción de un sistema de monitoreo de signos vitales. (Tesis en Pregrado De Ingeniería en comunicaciones y Electrónica), Departamento De Ingeniería en comunicaciones y Electrónica, Instituto Politécnico Nacional, Escuela Superior De Ingeniería Mecánica y Eléctrica, México D.F.
- Industria y Comercio. (2019). Organización internacional de métrologia legal (OIML). Disponible en: https://www.sic.gov.co/oiml
- Lehman, L. H. et al. (2015). "A Physiological Time Series Dynamics- Based Approach to Patient Monitoring and Outcome Prediction," in IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 1068-1076.
- Loureiro, R.(2015). Estudio plataformas IoT, Universitat Oberta de Catalunya. http://openaccess.uoc.edu/webapps/o2/bitstream/10609/42812/6/rloureiroTFC0615memoria.pdf
- Mathworks. (2020). React to channel activity with notification from IFTTT. Disponible en: https://www.mathworks.com/help/thingspeak/use-ifttt-to-send-text-message-notification.html
- Nasiri, S., Sadoughi, F., Tadayon, M. H., & Dehnad, A. (2019). Security Requirements of Internet of Things-Based Healthcare System: a Survey Study. Acta informatica medica: AIM: journal of the Society for Medical Informatics of Bosnia & Herzegovina: casopis Drustva za medicinsku informatiku BiH, 27(4), 253–258. https://doi.org/10.5455/aim.2019.27.253-258
- NXP. (2012). Blood Pressure Monitor Fundamentals and Design. Disponible en: https://www.nxp.com/docs/en/applicationnote/AN4328.pdf
- OCEANO. (1996). Autodicactica oceano color volumen VI. Barcelona, Barc: OCEANO GRUPO EDITORIAL ISBN: 84-7764-930-8.
- Onion Corporation. (2020). Onion Omega 2 Documentation. Disponible en: https://docs.onion.io/omega2-docs/omega2p.html
- Ordunez, P. (2018). Hearts in the Americas: Hearts en Cuba. TEMAS DE SALUD. http://temas.sld.cu/hipertension/tag/oms/
- Rodrigues, J. J. et al. (2018). "Enabling Technologies for the Internet of Health Things," in IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 13129-13141, 2018, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2789329.
- Vélez, A. (2019). Arquitecturas de referencia para IoT con trasnferencia segura de información. (Tesis en Especialización De Seguridad Informática), Escuela De Ciencias Básicas, Tecnlogía e Ingeniería, Universidad Nacional abierta y a diastancia, Tulua.




