Incorporation of eta sludge as a partial substitute of the fine aggregate in leaked concrete blocks
Incorporación de lodos de eta como sustituto parcial del árido fino en bloques de hormigón con fugas

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright statement
The authors exclusively assign to the Universidad EIA, with the power to assign to third parties, all the exploitation rights that derive from the works that are accepted for publication in the Revista EIA, as well as in any product derived from it and, in in particular, those of reproduction, distribution, public communication (including interactive making available) and transformation (including adaptation, modification and, where appropriate, translation), for all types of exploitation (by way of example and not limitation : in paper, electronic, online, computer or audiovisual format, as well as in any other format, even for promotional or advertising purposes and / or for the production of derivative products), for a worldwide territorial scope and for the entire duration of the rights provided for in the current published text of the Intellectual Property Law. This assignment will be made by the authors without the right to any type of remuneration or compensation.
Consequently, the author may not publish or disseminate the works that are selected for publication in the Revista EIA, neither totally nor partially, nor authorize their publication to third parties, without the prior express authorization, requested and granted in writing, from the Univeridad EIA.
Show authors biography
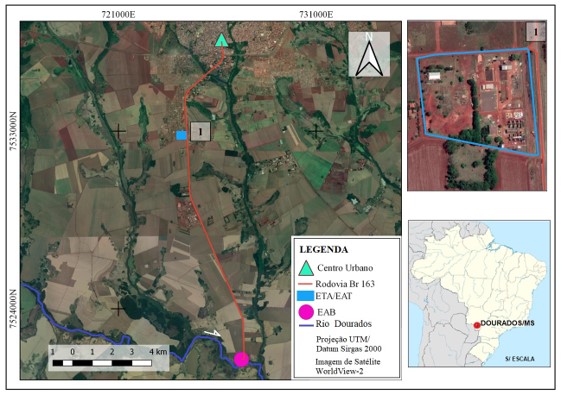
The increase in population concentration in urban areas has led to an increase in the demand for drinking water, consequently, the need to increase the production of treated water, forcing sanitation companies to expand their water treatment and distribution systems, resulting in the use of a greater volume of groundwater and surface water. However, surface water needs a treatment process to make it drinkable. This process, carried out in Water Treatment Stations - ETA, generates a hazardous solid waste, called ETA sludge. A major challenge faced by sanitation companies is the final disposal of ETA Sludge, as inadequate disposal, in addition to degrading the environment, is characterized as an environmental crime. The present work aims to obtain an alternative way of disposing of the ETA sludge from the Cecilia Leite Kirchener Water Treatment Station, in Dourados/MS. A study was carried out on the feasibility of incorporating ETA sludge, in replacement of fine aggregate (sand), in various proportions, for the manufacture of single concrete hollow blocks for sealing, produced on an industrial scale, carrying out various tests and analyses. laboratory tests. The results show that the ETA sludge from Dourados/MS presents technical feasibility to be used in the manufacture of concrete sealing blocks used in civil construction, in replacement of fine aggregate (sand), aiming at a correct destination for a solid hazardous waste. This study showed satisfactory results, since there was an increase in the strength of the blocks when compared to those without the addition of sludge, produced industrially.
Article visits 346 | PDF visits 141
Downloads
- ACHON, C. L.; BARROSO, M. M.; CORDEIRO, J. S. Resíduos de estações de tratamento de água e a ISO 24512: desafio do saneamento brasileiro. Revista Engenharia Sanitária e Ambiental, v. 18, n. 2, p. 115-122, 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1413-41522013000200003.
- ARAÚJO, F. C. ALBUQUERQUE, A. ANGELIM, R.R. Caracterização física do resíduo de uma estação de tratamento de água para sua utilização em materiais de construção. Revista Cerâmica, v. 61, p. 450-456, 2015. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0366-69132015613601931.
- ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILERA DE NORMAS TÉCNICAS (ABNT). NBR 10004: Resíduos sólidos – Classificação TÉCNICAS, A. B. D. N. Brasil: 71 p. 2004.
- ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILERA DE NORMAS TÉCNICAS (ABNT). NBR 12118: Blocos vazados de concreto simples para alvenaria –Métodos de ensaio. Rio de Janeiro: ABNT, 2013.
- ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILERA DE NORMAS TÉCNICAS (ABNT). NBR 6136: Blocos vazados de concreto simples para alvenaria – Requisitos. Rio de Janeiro: ABNT, 2007.
- ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILERA DE NORMAS TÉCNICAS (ABNT). NBR 7173: Blocos vazados de concreto simples para alvenaria sem função estrutural. Rio de Janeiro, 1982.
- ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILERA DE NORMAS TÉCNICAS (ABNT). NBR 7184: Análise Granulométrico – Solos. Rio de Janeiro 1984.
- ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILERA DE NORMAS TÉCNICAS (ABNT). NBR 9778: Argamassa e concreto endurecidos –Determinação da absorção de água por imersão –índice de vazios e massa específica –Método de ensaio. Rio de Janeiro, 1987.
- BITTENCOURT, S. et al. Aplicação de lodos de estações de tratamentos de água e de tratamento de esgoto em solo degradado. Revista Engenharia Sanitária e Ambiental, v. 17, n. 3, p. 315-324, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-41522012000300008.
- BRASIL. Sistema Nacional de Informações sobre Saneamento (SNIS). 24º Diagnóstico dos serviços de Água e Esgoto. Brasília: SNIS, 2019.
- DOURADOS. Plano Municipal de Saneamento Básico - PMSB. Dourados, p. 190. 2019. Disponível em: http://www.dourados.ms.gov.br/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/PRODUTO_6_INDICADORES_PMSB_DOURADOS.pdf. Acesso em 20 jan. 2019.
- HOPPEN, C. et al. Co-disposição de lodo centrifugado de Estação de Tratamento de Água (ETA) em matriz de concreto: método alternativo de preservação ambiental. Revista Cerâmica, v. 51, n. 318, p. 85-95, 2005. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0366-69132005000200003.
- PINHEIRO, B. C. A.; ESTEVÃO, G. M.; SOUZA, D. P. Lodo proveniente da estação de tratamento de água do município de Leopoldina, MG, para aproveitamento na indústria de cerâmica vermelha Parte I: caracterização do lodo. Revista Matéria (Rio de Janeiro), v. 19, p. 204-211, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-70762014000300003.
- RODRIGUES, L. P.; HOLANDA, J. N. F. Influence of the incorporation of water treatment plant (WTP) sludge on the technological properties of soil-cement bricks. Revista Cerâmica, v. 59, n. 352, p. 551-556, 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0366-69132013000400010.




