Playful learning strategy for the control of production systems from a Lean approach: The use of the Kanban card system
Estrategia lúdica de aprendizaje para el control de sistemas de producción desde un enfoque Lean: El uso del sistema de tarjetas Kanban

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright statement
The authors exclusively assign to the Universidad EIA, with the power to assign to third parties, all the exploitation rights that derive from the works that are accepted for publication in the Revista EIA, as well as in any product derived from it and, in in particular, those of reproduction, distribution, public communication (including interactive making available) and transformation (including adaptation, modification and, where appropriate, translation), for all types of exploitation (by way of example and not limitation : in paper, electronic, online, computer or audiovisual format, as well as in any other format, even for promotional or advertising purposes and / or for the production of derivative products), for a worldwide territorial scope and for the entire duration of the rights provided for in the current published text of the Intellectual Property Law. This assignment will be made by the authors without the right to any type of remuneration or compensation.
Consequently, the author may not publish or disseminate the works that are selected for publication in the Revista EIA, neither totally nor partially, nor authorize their publication to third parties, without the prior express authorization, requested and granted in writing, from the Univeridad EIA.
Show authors biography
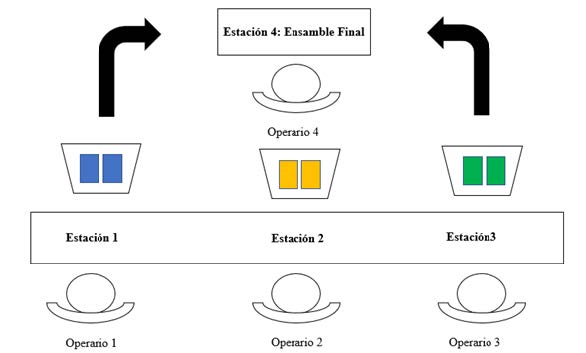
Currently, organizations constantly seek greater productivity in their processes in order to guarantee their sustainability in the market. The Lean Manufacturing philosophy seeks to eradicate activities that do not add value to the processes and that generate financial losses for companies. In this document, a playful learning strategy is proposed, the purpose of which is to explain a production control system from a lean manufacturing approach known as the Kanban card system. The game was carried out in different settings, such as the Ninth National Meeting of the Iddeal Network and the Third meeting of games in engineering, held at the Corporación Universitaria Minuto de Dios, Buga Regional Center. In these spaces, the participation of professionals and students in the training cycle of the industrial engineering program was evidenced. The play was directed by the members of the GLIOSP research seedbed of the same program. Among the most relevant results is the strengthening of the concept of just-in-time philosophy in the participants of the play, while generating a clear path for the implementation of the Kanban card system in production systems.
Article visits 566 | PDF visits 436
Downloads
- Cáceres-Gelvez, S., Arango-Serna, M. D., & Zapata-Cortés, J. A. (2022). A conceptual framework for integrating Facility Layout and Production Scheduling in Flowshop Manufacturing Cells decisions. Revista EIA, 19(38), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.24050/reia.v19i38.1543
- Chepin, E. (2021). Robotics: From first-order cybernetics to third-order cybernetics. Procedia Computer Science, 190(2019), 130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2021.06.016
- Chiarini, A. (2013). The Main Methods of Lean Organization: Kanban, Cellular Manufacturing, SMED and TPM. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-88-470-2510-3_6
- De Vin, L. J., Jacobsson, L., Odhe, J. E., & Wickberg, A. (2017). Lean Production Training for the Manufacturing Industry: Experiences from Karlstad Lean Factory. Procedia Manufacturing, 11(June), 1019–1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2017.07.208
- Gaete-Quezada, R. A. (2011). El juego de roles como estrategia de evaluación de aprendizajes universitarios University education. Educación y Educadores, 14(2), 289–307.
- Gómez Giraldo, L. F., & López Rivera, Y. M. (2018). Propuesta lúdica como herramienta de apoyo al proceso enseñanza – aprendizaje en el estudio del trabajo, enfocada a la estandarización de tiempos. Ingenierías USBMed, 9(2), 34–43. https://doi.org/10.21500/20275846.3576
- Gopi, S., Suresh, A., & John Sathya, A. (2019). Value stream mapping & Manufacturing process design for elements in an auto-ancillary unit-A case study. Materials Today: Proceedings, 22, 2839–2848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.03.416
- Hernández-Reinoza, H. J., Villota-Ibarra, C., & Jiménez-Builes, J. A. (2021). Metodología lúdica para la enseñanza de la ingeniería de requisitos basada en esquemas preconceptuales. Revista EIA, 18(35). https://doi.org/10.24050/reia.v18i35.1394
- Krajewski, L. J., Ritzman, L. P., & Malhotra, M. K. (2008). Administración de Operaciones: Procesos y cadena de valor.
- Omogbai, O., & Salonitis, K. (2017). The Implementation of 5S Lean Tool Using System Dynamics Approach. Procedia CIRP, 60, 380–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.01.057
- O’Reilly, K., Ruokis, S., Russell, K., Teves, T., DiLibero, J., Yassa, D., Berry, H., & Howell, M. D. (2016). Standard work for room entry: Linking lean, hand hygiene, and patient-centeredness. Healthcare, 4(1), 45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hjdsi.2015.12.008
- Palange, A., & Dhatrak, P. (2021). Lean manufacturing a vital tool to enhance productivity in manufacturing. Materials Today: Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.193
- Paredes-Rodríguez, A. M. (2017). Aplicación de la herramienta Value Stream Mapping a una empresa embaladora de productos de vidrio. Entramado, 13(1), 262–277. https://doi.org/10.18041/entramado.2017v13n1.25103
- Paredes-Rodríguez, A. M., Peláez-Mejía, K. A., & Salazar-Ramos, A. F. (2016). Propuesta de un juego de mesa como herramienta didáctica para la explicación de conceptos de control de inventarios en programas de ingeniería industrial. Educación En Ingeniería, 11(21), 45–50.
- Peláez Mejía, K. A., Payán Quevedo, J. L., & Salazar Ramos, A. F. (2016). Herramienta didáctica para la explicación de conceptos de balanceo de línea en cursos de producción de los programas de ingeniería industrial. Revista Educación En Ingeniería, 11(21), 51–58.
- Puche, J., Costas, J., Ponte, B., Pino, R., & de la Fuente, D. (2019). The effect of supply chain noise on the financial performance of Kanban and Drum-Buffer-Rope: An agent-based perspective. Expert Systems with Applications, 120, 87–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.11.009
- Ribeiro, P., Sá, J. C., Ferreira, L. P., Silva, F. J. G., Pereira, M. T., & Santos, G. (2019). The impact of the application of lean tools for improvement of process in a plastic company: A case study. Procedia Manufacturing, 38(2019), 765–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2020.01.104
- Rivera Cadavid, L. (2011). Justificación conceptual de un modelo de implementación de Lean Manufacturing. Heurística, 15, 91–106.
- Serje Gutierrez, V., Prieto Patiño, L. E., & Riveros Munévar, F. (2021). Actitudes hacia la ciencia y la investigación en miembros de instituciones de educación superior de Bogotá: diferencias por variables demográficas y de rol académico. Educación y Educadores, 24(3), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.5294/edu.2021.24.3.1
- Singh, H., Bahl, A., Kumar, A., & Mann, G. S. (2018). Materials and Information Flow Analysis and Optimization of Manufacturing Processes in MSMEs by the Application of Value Stream Mapping
- (VSM) Technique. Materials Today: Proceedings, 5(14), 28420–28426.
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.10.128
- Talanquer, V. (2015). The importance of formative assessment. Educacion Quimica, 26(3), 177–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eq.2015.05.001
- Trevisan, L., Peruccio, P. P., & Barbero, S. (2018). From engineering to industrial design: Issues of educating future engineers to systemic design. Procedia CIRP, 70, 319–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2018.02.014
- Varadejsatitwong, P., Banomyong, R., & Julagasigorn, P. (2022). A Proposed Performance-Measurement System for Enabling Supply-Chain Strategies. Sustainability (Switzerland), 14(19). https://doi.org/10.3390/su141911797
- Yıldız, B., & Ustaoğlu, M. (2012). Optimal Production Model for EVs Manufacturing Process in Turkey: A Comparable Case of EMQ/JIT Production Models for EVs’ Battery Production. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 58, 1482–1490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.09.1135




