Process simulation and environmental assessment of the mass production of a modified bioadsorbent with chelants and magnetic nanoparticles
Simulación de procesos y evaluación ambiental de la producción de un bioadsorbente modificado con quelantes y nanopartículas magnéticas

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright statement
The authors exclusively assign to the Universidad EIA, with the power to assign to third parties, all the exploitation rights that derive from the works that are accepted for publication in the Revista EIA, as well as in any product derived from it and, in in particular, those of reproduction, distribution, public communication (including interactive making available) and transformation (including adaptation, modification and, where appropriate, translation), for all types of exploitation (by way of example and not limitation : in paper, electronic, online, computer or audiovisual format, as well as in any other format, even for promotional or advertising purposes and / or for the production of derivative products), for a worldwide territorial scope and for the entire duration of the rights provided for in the current published text of the Intellectual Property Law. This assignment will be made by the authors without the right to any type of remuneration or compensation.
Consequently, the author may not publish or disseminate the works that are selected for publication in the Revista EIA, neither totally nor partially, nor authorize their publication to third parties, without the prior express authorization, requested and granted in writing, from the Univeridad EIA.
Show authors biography
Residue recovery approaches are essential to achieving more green production in seafood industry. Chitosan is a biopolymer with multiple purposes in sectors such as agriculture, foodindustry, cosmetics, water treatment systems, among others. Wastes from the shellfish
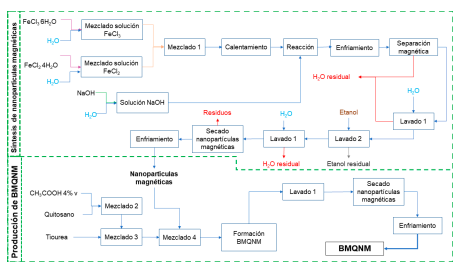
industry can be employed in the synthesis of chitosan, turn out to be an alternative for waste recovery. One of the alternative uses of chitosan is as precursor for the production of modified bioadsorbents for removing pollutants. In this work, the environmental assessment of the production process on an industrial scale of chitosan microbead modified with magnetite nanoparticles and thiourea was developed for evaluating the posible environmental impacts. The software Aspen Plus® was used for the process simulation, that allows the quantification of mass flows and estimation of properties. The environmental evaluation was done by using the WAste Reduction (WAR) algorithm, through the WAR GUI software. The results showed that the process consumes potential environmental impacts (PEI), obtaining a positive value of 1,870 PEI/h. The categories related to toxicological impacts (HTPI, HTPE, TTP and ATP) presented lower values than the related to atmospheric impacts (GWP, ODP, PCOP and AP), with the greatest contribution being human toxicity by ingestion (HTPI) and toxicity terrestrial potential (TTP), which are associated with the median lethal dose (LD50) of the compounds involved in the process. PEI consumption was determined by using as energetic source natural gas.
Article visits 225 | PDF visits 163
Downloads
- Acosta-Ferreira, S., Castillo, O. S., Madera-Santana, J. T., Mendoza-García, D. A., Núñez-Colín, C. A., Grijalva-Verdugo, C., Villa-Lerma, A. G., Morales-Vargas, A. T., & Rodríguez-Núñez, J. R. (2020). Production and physicochemical characterization of chitosan for the harvesting of wild microalgae consortia. Biotechnology Reports, 28, e00554. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BTRE.2020.E00554
- Aguilar Vásquez, E., & González-Delgado, Á. (2021). Evaluación ambiental de la producción de microperlas de quitosano modificadas con TiO2 y magnetita usando el algoritmo de reducción de residuos (WAR). Revista ION, 34(1), 121–136. https://doi.org/10.18273/revion.v34n1-2021010
- Alfaro, I., Molina, L., González, P., Gaete, J., Valenzuela, F., Marco, J. F., Sáez, C., & Basualto, C. (2019). Silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles functionalized with betaine and their use as an adsorbent for Mo(VI) and Re(VII) species from acidic aqueous solutions. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 78, 271–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.06.002
- Arteaga-Díaz, S., Sanjuan-Acosta, M. J., & González-Delgado, Á. (2018). Computer-aided environmental evaluation of bioethanol production from empty palm fruit bunches using oxalic acid pretreatment and molecular sieves. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 70, 2113–2118. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1870353
- Asab, G., Zereffa, E. A., & Abdo Seghne, T. (2020). Synthesis of Silica-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles by Microemulsion Method: Characterization and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity. International Journal of Biomaterials, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4783612
- Bilal, M., Ihsanullah, I., Younas, M., & Ul Hassan Shah, M. (2021). Recent advances in applications of low-cost adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals from water: A critical review. Separation and Purification Technology, 278, 119510. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SEPPUR.2021.119510
- Bui, T. Q., Ton, S. N. C., Duong, A. T., & Tran, H. T. (2018). Size-dependent magnetic responsiveness of magnetite nanoparticles synthesised by co-precipitation and solvothermal methods. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices, 3(1), 107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2017.11.002
- Carlson, E. C. (1996). Don’t Gamble With Physical Properties. Chemical Engineering Progress, October, 35–46.
- Chai, W. S., Cheun, J. Y., Kumar, P. S., Mubashir, M., Majeed, Z., Banat, F., Ho, S. H., & Show, P. L. (2021). A review on conventional and novel materials towards heavy metal adsorption in wastewater treatment application. Journal of Cleaner Production, 296, 126589. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2021.126589
- Cogollo-Herrera, K., Bonfante-Álvarez, H., De Ávila-Montiel, G., Barros, A. H., & González-Delgado, Á. D. (2018). Techno-economic sensitivity analysis of large scale chitosan production process from shrimp shell wastes. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 70, 2179–2184. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1870364
- Dos Santos, L. N., Santos, A. S., Dantas, K. D. G. F., & Ferreira, N. R. (2022). Adsorption of Cu (II) Ions Present in the Distilled Beverage (Sugar Cane Spirit) Using Chitosan Derived from the Shrimp Shell. Polymers 2022, Vol. 14, Page 573, 14(3), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM14030573
- González-Delgado, A., Cartagena, U. de, & SENA, S. N. de A. (2016). Remoción de Hidrocarburos aromáticos policíclicos (HAPs), presentes en aguas costeras de la bahía de Cartagena mediante la utilización de exoesqueleto de camarón como fuente de bioadsorbentes modificados con nanoparticulas (p. 30).
- González-Delgado, Á. D., Moreno-sader, K. A., & Martínez-Consuegra, J. D. (2022). Biorrefinación sostenible del camarón : desarrollos desde la Ingeniería de Procesos Asistida por Computador.
- Hadadian, Y., Sampaio, D. R. T., Ramos, A. P., Carneiro, A. A. O., Mozaffari, M., Cabrelli, L. C., & Pavan, T. Z. (2018). Synthesis and characterization of zinc substituted magnetite nanoparticles and their application to magneto-motive ultrasound imaging. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 465(May), 33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.05.069
- IDEAM. (2018). Carácterísticas Climatológicas De Ciudades Principales Y Municipios Turísticos. Instituto de Hidrología, Meteorología y Estudios Ambientales, 48. https://doi.org/http://www.ideam.gov.co/documents/21021/21789/1Sitios+turisticos2.pdf/cd4106e9-d608-4c29-91cc-16bee9151ddd
- Karimi, M. H., Mahdavinia, G. R., Massoumi, B., Baghban, A., & Saraei, M. (2018). Ionically crosslinked magnetic chitosan/κ-carrageenan bioadsorbents for removal of anionic eriochrome black-T. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 113, 361–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.02.102
- Kou, S. (Gabriel), Peters, L. M., & Mucalo, M. R. (2021). Chitosan: A review of sources and preparation methods. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 169, 85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2020.12.005
- Li, J. L., Li, D. C., Zhang, S. L., Cui, H. C., & Wang, C. (2011). Analysis of the factors affecting the magnetic characteristics of nano-Fe 3 O 4 particles. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56(8), 803–810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-010-4126-z
- Meramo-Hurtado, S., Urbina-Suaréz, N., & González-Delgado, Á. (2019). Computer-aided environmental and exergy analyses of a large-scale production of chitosan microbeads modified with TiO2 nanoparticles. Journal of Cleaner Production, 237, 117804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117804
- Miron, A., Sarbu, A., Zaharia, A., Sandu, T., Iovu, H., Fierascu, R. C., Neagu, A.-L., Chiriac, A.-L., & Iordache, T.-V. (2022). A Top-Down Procedure for Synthesizing Calcium Carbonate-Enriched Chitosan from Shrimp Shell Wastes. Gels, 8(11), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/GELS8110742
- Moreno-Sader, K. A., Martínez-Consuegra, J., & González-Delgado, Á. D. (2021). An integrated biorefinery approach via material recycle/reuse networks for the extraction of value-added components from shrimp: Computer-aided simulation and environmental assessment. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 127, 443–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FBP.2021.04.003
- Moreno-Sader, K., Meramo-Hurtado, S., & González-Delgado, A. (2019). Computer-aided environmental and exergy analysis as decision-making tools for selecting bio-oil feedstocks. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 112(February), 42–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.05.044
- Niculescu, A. G., Chircov, C., & Grumezescu, A. M. (2022). Magnetite nanoparticles: Synthesis methods – A comparative review. Methods, 199, 16–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.YMETH.2021.04.018
- Okolie, J. A., Nanda, S., Dalai, A. K., & Kozinski, J. A. (2021). Techno-economic evaluation and sensitivity analysis of a conceptual design for supercritical water gasification of soybean straw to produce hydrogen. Bioresource Technology, 331, 125005. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2021.125005
- Pereira da Silva, A. K., Cardoso, A., Benício de Sá Filho, E., Monteiro Cordeiro de Azeredo, H., Freire, F., Casimiro Filho, F., & Brito de Figueirêdo, M. C. (2021). Integrating life cycle assessment in early process development stage: The case of extracting starch from mango kernel. Journal of Cleaner Production, 321, 128981. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2021.128981
- Pourmortazavi, S. M., Sahebi, H., Zandavar, H., & Mirsadeghi, S. (2019). Fabrication of Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated by extracted shrimp peels chitosan as sustainable adsorbents for removal of chromium contaminates from wastewater: The design of experiment. Composites Part B: Engineering, 175(June), 107130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107130
- Qamar, S. A., Ashiq, M., Jahangeer, M., Riasat, A., & Bilal, M. (2020). Chitosan-based hybrid materials as adsorbents for textile dyes–A review. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering, 2, 100021. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CSCEE.2020.100021
- Qiu, N., Liu, Y., Xiang, M., Lu, X., Yang, Q., & Guo, R. (2018). A facile and stable colorimetric sensor based on three-dimensional graphene/mesoporous Fe3O4 nanohybrid for highly sensitive and selective detection of p-nitrophenol. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 266, 86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2018.03.059
- Rinaudo, M. (2006). Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Progress on Polymer Science, 31, 603–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2006.06.001
- Santos, V. P., Marques, N. S. S., Maia, P. C. S. V., de Lima, M. A. B., Franco, L. de O., & de Campos-Takaki, G. M. (2020). Seafood Waste as Attractive Source of Chitin and Chitosan Production and Their Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(12), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS21124290
- Simsir, H., Eltugral, N., & Karagoz, S. (2017). Hydrothermal carbonization for the preparation of hydrochars from glucose, cellulose, chitin, chitosan and wood chips via low-temperature and their characterization. Bioresource Technology, 246, 82–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.018
- Singh, A., Benjakul, S., & Prodpran, T. (2019). Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Chitosan from Squid Pen: Molecular Characterization and Fat Binding Capacity. Journal of Food Science, 84(2), 224–234. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.14439
- Singh, S., Negi, T., Sagar, N. A., Kumar, Y., Tarafdar, A., Sirohi, R., Sindhu, R., & Pandey, A. (2022). Sustainable processes for treatment and management of seafood solid waste. Science of The Total Environment, 817, 152951. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.152951
- Soares, S. F., Fernandes, T., Trindade, T., & Daniel-da-Silva, A. L. (2019). Recent advances on magnetic biosorbents and their applications for water treatment. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 18(1), 151–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10311-019-00931-8
- Tao, K., Dou, H., & Sun, K. (2008). Interfacial coprecipitation to prepare magnetite nanoparticles : Concentration and temperature dependence. 320, 115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2008.01.051
- Teixeira-Costa, B. E., & Andrade, C. T. (2021). Chitosan as a Valuable Biomolecule from Seafood Industry Waste in the Design of Green Food Packaging. Biomolecules, 11(11), 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/BIOM11111599
- Vakili, M., Rafatullah, M., Ibrahim, M. H., & Abdullah, A. Z. (2016). Preparation of Chitosan Beads for the Adsorption of Reactive Blue 4 from Aqueous Solutions. Iranica Journal of Energy and Environment, January. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.ijee.2016.07.02.06
- Yarnpakdee, S., Kaewprachu, P., Jaisan, C., Senphan, T., Nagarajan, M., & Wangtueai, S. (2022). Extraction and Physico–Chemical Characterization of Chitosan from Mantis Shrimp (Oratosquilla nepa) Shell and the Development of Bio-Composite Film with Agarose. Polymers, 14(19), 3983. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM14193983
- Yazdani, F., & Edrissi, M. (2010). Effect of pressure on the size of magnetite nanoparticles in the coprecipitation synthesis. Materials Science & Engineering B, 171(1–3), 86–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2010.03.077
- Young, D. M., & Cabezas, H. (1999). Designing sustainable processes with simulation: the waste reduction (WAR) algorithm. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 23, 1477–1491.
- Zhou, L., Liu, J., & Liu, Z. (2009). Adsorption of platinum ( IV ) and palladium ( II ) from aqueous solution by thiourea-modified chitosan microspheres. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172, 439–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.030
- Zuorro, A., Moreno-Sader, K. A., & González-Delgad, Á. D. (2021). Inherent Safety Analysis and Sustainability Evaluation of Chitosan Production from Shrimp Exoskeleton in Colombia. Water, 13(4), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/W13040553




