The single inductor dual buck inverter: voltage control and procedure to obtain mathematical model
El inversor dual buck de inductor simple: control de voltaje y procedimiento para obtener su modelo matemático

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright statement
The authors exclusively assign to the Universidad EIA, with the power to assign to third parties, all the exploitation rights that derive from the works that are accepted for publication in the Revista EIA, as well as in any product derived from it and, in in particular, those of reproduction, distribution, public communication (including interactive making available) and transformation (including adaptation, modification and, where appropriate, translation), for all types of exploitation (by way of example and not limitation : in paper, electronic, online, computer or audiovisual format, as well as in any other format, even for promotional or advertising purposes and / or for the production of derivative products), for a worldwide territorial scope and for the entire duration of the rights provided for in the current published text of the Intellectual Property Law. This assignment will be made by the authors without the right to any type of remuneration or compensation.
Consequently, the author may not publish or disseminate the works that are selected for publication in the Revista EIA, neither totally nor partially, nor authorize their publication to third parties, without the prior express authorization, requested and granted in writing, from the Univeridad EIA.
Show authors biography
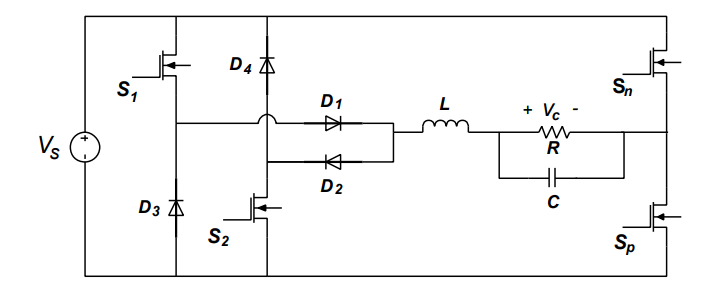
In this article, the procedure to obtain the mathematical model for a 2 KW DBI (Dual Buck Inverter) converter, which can be used in renewable energy applications, is described. In the same way, the operation modes of this inverter are described with the respective equations that model its behavior for each one of them and, with the activation signals of the MOSFETs present in the inverter, the switched model is created. The linearization procedure of the model at one operating point is shown, simulation results are recorded in Matlab®/Simulink™ using PID controller, making changes in both load and input DC voltage levels for the proposed model and for the inverter circuit, thus making use of discrete elements. The total harmonic distortion in the output voltage signal is less than 0.73%, complying with the IEEE 519 standard.
Article visits 192 | PDF visits 128
Downloads
- Bacha, S., Munteanu, I. and Bratcu, A. I. (2014) ‘Power Electronic Converters Modeling and Control’, Advanced Textbooks in Control and Signal Processing. London: Springer. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4471-5478-5.
- Chen, B. et al. (2013) ‘Current distortion correction in dual buck photovoltaic inverter with a novel PWM modulation and control method’, Conference Proceedings - IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition - APEC, pp. 727–731. doi: 10.1109/APEC.2013.6520290.
- Cho, Y. (2017) ‘Dual-buck residential photovoltaic inverter with a high-accuracy repetitive current controller’, Renewable Energy. Elsevier Ltd, 101, pp. 168–181. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2016.08.050.
- Feng, H. et al. (2009) ‘Three level dual Buck half bridge inverter’, 2009 International Conference on Sustainable Power Generation and Supply, pp. 1–5. doi: 10.1109/SUPERGEN.2009.5347984.
- Hong, F. et al. (2015) ‘Single Inductor Dual Buck Full-Bridge Inverter’, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 62(8), pp. 4869–4877. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2399280.
- ‘IEEE Recommended Practice and Requirements for Harmonic Control in Electric Power Systems’ (2014) IEEE Std 519-2014 (Revision of IEEE Std 519-1992), pp. 1–29. doi: 10.1109/IEEESTD.2014.6826459.
- Liu, J. and Yan, Y. (2003) ‘A novel hysteresis current controlled dual buck half bridge inverter’, IEEE 34th Annual Conference on Power Electronics Specialist, 2003. PESC ’03., 4, pp. 1615–1620. doi: 10.1109/PESC.2003.1217699.
- Moreno-Munoz, A. et al. (2011) ‘Energy efficiency criteria in uninterruptible power supply selection’, Applied Energy, 88(4), pp. 1312–1321. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.08.017.
- Muhammad, E. (2010) ‘Sliding Mode Control of Dual-Buck Full-Bridge Inverter’, Engineering, (1), pp. 1–2.
- Rashid, M. H. (2004) ‘Electrónica de Potencia’, Circuitos, Dispositivos y Aplicaciones. Segunda Ed. México: Pearson Educación.
- Su, T. et al. (2015) ‘A High Power Density Dual-buck Full-bridge Inverter Based on Carrier Phase-shifted SPWM Control’, pp. 1715–1721.
- Wang, B. and Yi, L.-Z. (2011) ‘Control study of Dual-BUCK grid-connected inverter based on least squares algorithm’, 2011 Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, APPEEC 2011 - Proceedings, pp. 0–3. doi: 10.1109/APPEEC.2011.5749072.
- Wang, L. et al. (2017) ‘Dual buck grid-connected inverter based on GaN devices’, 2016 Asian Conference on Energy, Power and Transportation Electrification, ACEPT 2016, (2014). doi: 10.1109/ACEPT.2016.7811515.
- Wang, Z., Xiao, L. and Yan, G. (2006) ‘Simulation study of charge controlled half-cycle modulated dual buck half bridge inverter’, PESC Record - IEEE Annual Power Electronics Specialists Conference, (1). doi: 10.1109/PESC.2006.1711821.
- Xie, J. et al. (2014) ‘A novel high power density dual-buck inverter with coupled filter inductors’, in IECON 2014 - 40th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, pp. 1111–1117. doi: 10.1109/IECON.2014.7048641.
- Yao, Z. (2009) ‘Two-switch dual-buck grid-connected inverter’, 2009 IEEE 6th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, IPEMC ’09, 3, pp. 2182–2187. doi: 10.1109/IPEMC.2009.5157764.
- Yao, Z. et al. (2010) ‘Dual-buck full-bridge inverter with SPWM control and single current sensor’, Proceedings of the 2010 5th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, ICIEA 2010, 1, pp. 2154–2158. doi: 10.1109/ICIEA.2010.5515165.
- Yao, Zhilei and Hu, G. (2011) ‘Comparison of dual-buck full-bridge inverter with different inductor structures’, Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, APPEEC, pp. 1–3. doi: 10.1109/APPEEC.2011.5747724.
- Yao, Z and Hu, G. (2011) ‘Comparison of Dual-Buck Full-Bridge Inverter with Different Inductor Structures’, in 2011 Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, pp. 1–3. doi: 10.1109/APPEEC.2011.5747724.
- Yao, Z., Hu, G. and Chen, R. (2010) ‘Improved Control Strategy for Dual-Buck Full-Bridge Inverter with Single Current Sensor’, in 2010 Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, pp. 1–4. doi: 10.1109/APPEEC.2010.5448357.
- Yao, Z., Hu, G. and Chen, R. (2012) ‘Two-switch dual-buck grid-connected inverter with hysteresis current control’, 2010 Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, 27(7), pp. 3310–3318. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2011.2179318.
- Yao, Z., Xiao, L. and Yan, Y. (2009) ‘Dual-buck full-bridge inverter with hysteresis current control’, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 56(8), pp. 3153–3160. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2022072.
- Zhang, X. and Song, Y. (2011) ‘A control method of dual buck half bridge inverter based on the phase of voltage loop output’, Proceedings - 3rd International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation, ICMTMA 2011, 1(2), pp. 25–27. doi: 10.1109/ICMTMA.2011.13.
- Zhou, L. and Gao, F. (2016) ‘Dual buck inverter with series connected diodes and single inductor’, Conference Proceedings - IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition - APEC, 2016-May(c), pp. 2259–2263. doi: 10.1109/APEC.2016.7468180.




