Computational thinking definitions. A review of the literatura
Definiciones del pensamiento computacional. Una revisión de la literatura

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright statement
The authors exclusively assign to the Universidad EIA, with the power to assign to third parties, all the exploitation rights that derive from the works that are accepted for publication in the Revista EIA, as well as in any product derived from it and, in in particular, those of reproduction, distribution, public communication (including interactive making available) and transformation (including adaptation, modification and, where appropriate, translation), for all types of exploitation (by way of example and not limitation : in paper, electronic, online, computer or audiovisual format, as well as in any other format, even for promotional or advertising purposes and / or for the production of derivative products), for a worldwide territorial scope and for the entire duration of the rights provided for in the current published text of the Intellectual Property Law. This assignment will be made by the authors without the right to any type of remuneration or compensation.
Consequently, the author may not publish or disseminate the works that are selected for publication in the Revista EIA, neither totally nor partially, nor authorize their publication to third parties, without the prior express authorization, requested and granted in writing, from the Univeridad EIA.
Show authors biography
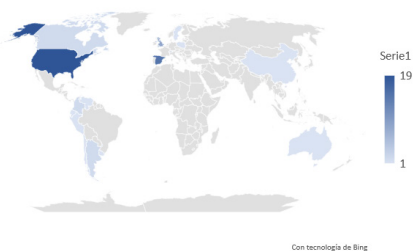
The purpose of this literature review was to perform an analysis of Computational Thinking (CT) definitions, aiming to find points of convergence among the 62 analyzed definitions. The publication year, authors, and country of origin of the first author were considered as variables to understand the behavior of the CT construct, assuming different perspectives proposed from 2006 to 2022. To achieve this purpose, five sources of information were reviewed, and 62 articles that presented a definition of CT were selected. According to the results, the years with the highest number of proposals were 2015 and 2017. The countries with the most publications featuring definitions were the United States, followed by Spain. The most representative authors were Jeannette Marie Wing, Cynthia Selby, and Francisco José García-Peñalvo. Regarding the analysis of the words, two lines stand out: one corresponds to approaches related to informatics, computing, technology, or programming, and the other assumes the absence of these terms. It is important to highlight the prominence of the word "problem(s)," which appeared with a frequency of 89% in the analyzed articles' definitions, and the word "solve(s)" with 54%. In line with the results, it is concluded that there is diversity in the proposals to define CT, making it challenging to find a point of convergence. Therefore, it is concluded that those interested in investigating the construct can adopt the definition that suits their research needs.
Article visits 257 | PDF visits 147
Downloads
- Aho, A.V. (2012) 'Computation and computational thinking', Computer Journal, 55(7), pp. 833-835. https://doi.org/10.1093/comjnl/bxs074
- Allsop, Y. (2019) 'Assessing computational thinking process using a multiple evaluation approach', International Journal of Child-Computer Interaction, 19, pp. 30-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcci.2018.10.004
- Anderson, N.D. (2016) 'A Call for Computational Thinking in Undergraduate Psychology', Psychology Learning and Teaching, 15(3), pp. 226-234. https://doi.org/10.1177/1475725716659252
- Barr, D., Harrison, J. and Conery, L. (2011) 'Computational Thinking: A Digital Age Skill for Everyone', Learning and Leading with Technology.
- Barr, V. and Stephenson, C. (2011) 'Bringing computational thinking to K-12: What is involved and what is the role of the computer science education community?', ACM Inroads, 2(1), pp. 48-54. https://doi.org/10.1145/1929887.1929905
- Basogain-Olabe, X., Olabe-Basogain, M.Á. and Olabe-Basogain, J.C. (2015) 'Pensamiento Computacional a través de la Programación: Paradigma de Aprendizaje', Revista de Educación a Distancia (RED), 46(46). https://doi.org/10.6018/red/46/6
- Basogain, X., Olabe, J., Rico, M., Rodríguez, L. and Miguel, A. (2017) 'Pensamiento computacional en las escuelas de Colombia', Researchgate, (July), p. 12.
- Bocconi, S., Chioccariello, A., Dettori, G., Ferrari, A., Engelhardt, K., Kampylis, P. and Punie, Y. (2016) 'El Pensamiento Computacional en la Enseñanza Obligatoria (Computhink) Implicaciones para la política y la práctica', Proceedings of the EdMedia 2016 Conference, (June), pp. 1-43. https://doi.org/10.2791/792158
- Bordignon, F. and Iglesias, A. (2019) Introducción al Pensamiento Computacional: Búsquedas y Ordenamiento.
- Brennan, K. (2011) 'Computational thinking Concepts'. Available at: http://scratched.gse.harvard.edu/resources/computational-thinking-concepts-march-2011-webinar.html (Accessed: 20 June 2024).
- Brennan, K. and Resnick, M. (2012) 'New frameworks for studying and assessing the development of computational thinking', Studies in Computational Intelligence, 727. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-64051-8_9
- Carmona-Mesa, J.A., Morales, S. and Villa-Ochoa, J.A. (2017) 'Pensamiento Computacional en la formación inicial de profesores de matemáticas', (December), p. 17. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.33696.07688
- Ceibal, P. (2017) '¿Qué aporta al aula el Pensamiento Computacional?'. Available at: https://www.ceibal.edu.uy/es/articulo/que-aporta-al-aula-el-pensamiento-computacional (Accessed: 20 June 2024).
- Chen, H.E., Sun, D., Hsu, T.C., Yang, Y. and Sun, J. (2023) 'Visualising trends in computational thinking research from 2012 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis', Thinking Skills and Creativity, 47(October 2022), 101224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2022.101224
- Codelearn (2019) '¿Qué es el pensamiento computacional?'. Available at: https://codelearn.es/blog/que-es-pensamiento-computacional/ (Accessed: 20 June 2024).
- Csizmadia, A., Curzon, P., Dorling, M., Humphreys, S., Ng, T., Selby, C. and Woollard, J. (2015) Computational Thinking: A Guide for Teachers. Computing At School.
- CSTA and ISTE (2011) 'Operational definition of computational thinking for K–12 education'. Available at: http://csta.acm.org/Curriculum/sub/CurrFiles/%0ACompThinkingFlyer.pdf (Accessed: 20 June 2024).
- Cummins, K. (2016) 'Five reasons why computational thinking is an essential tool for teachers and students'. Available at: https://www.edgalaxy.com/journal/2016/5/25/five-reasons-whycomputational-thinking-is-an-essential-tool-for-teachers-and-students (Accessed: 20 June 2024).
- Curzon, P. (2015) 'Computational thinking: Searching to speak'. Available at: https://cs4fndownloads.files.wordpress.com/2016/02/searchingtospeak-booklet.pdf (Accessed: 20 June 2024).
- Cutumisu, M., Adams, C. and Lu, C. (2019) 'A Scoping Review of Empirical Research on Recent Computational Thinking Assessments', Journal of Science Education and Technology, 28(6), pp. 651-676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-019-09799-3
- De Paula, B.H., Burn, A., Noss, R. and Valente, J.A. (2018) 'Playing Beowulf: Bridging computational thinking, arts and literature through game-making', International Journal of Child-Computer Interaction, 16, pp. 39-46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcci.2017.11.003
- Denning, P.J. (2009) 'The profession of IT: Beyond computational thinking', Communications of the ACM, 52(6), pp. 28-30. https://doi.org/10.1145/1516046.1516054
- European Council (2006) 'Recommendation of the European Parliament and the Council on key competencies for lifelong learning', Official Journal of the European Union, (March 2002), pp. 10-18.
- Formación en Red del INTEF (2017) '¿Qué es el pensamiento computacional?'. Available at: http://formacion.intef.es/pluginfile.php/87694/mod_imscp/content/9/qu_es_el_pensamiento_computacional.html (Accessed: 20 June 2024).
- Fraillon, J., Ainley, J., Schulz, W., Friedman, T. and Duckworth, D. (2018) Preparing for Study, life in a digital world: The IEA International Computer and Information Literacy 71, COMPUTERS IN THE SCHOOLS Educational. International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-38781-5
- García-Peñalvo, F.J. (2016) 'What Computational Thinking Is', Journal of Information Technology Research, 9(3), pp. v-viii. https://doi.org/10.1145/1539024.1509053
- García-Peñalvo, F., Reimann, D., Tuul, M., Rees, A. and Jormanainen, I. (2016) 'An overview of the most relevant literature on coding and computational thinking with emphasis on the relevant issues for teachers KA2 project "TACCLE 3 – Coding" (2015-1-BE02-KA201-012307)', (October), p. 72. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.13111.01440
- González-González, C.S. (2019) 'State of the art in the teaching of computational thinking and programming in childhood education', Education in the Knowledge Society, 20, pp. 1-15. https://doi.org/10.14201/eks2019_20_a17
- Google for Education (2017) 'Computational Thinking Overview'. Available at: http://edu.google.com/resources/programs/exploring-computationalthinking/#!Ct-overview (Accessed: 20 June 2024).
- Grover, S. and Pea, R. (2018) 'Computational Thinking: A Competency Whose Time Has Come', Computer Science Education, (December). https://doi.org/10.5040/9781350057142.ch-003
- Huerta Jimenéz, C.S. and Albo Velázquez, M. (2021) 'Pensamiento computacional como una habilidad genérica: una revisión sistemática', Ciencia Latina, 5(1), pp. 1055-1078.
- Iglesias, A. and Bordignon, F. (2020) Introducción al pensamiento computacional. (U.P.N. y E.SE., Ed.).
- International Society for Technology in Education (2015) CT leadership toolkit.
- Iturbide, J.Á.V. and Lope, M.M. (2021) 'Análisis del “pensamiento computacional” desde una perspectiva educativa', Revista de Educación a Distancia (RED), 21(68). https://doi.org/10.6018/red.484811
- Kalelioğlu, F., Gülbahar, Y. and Kukul, V. (2016) 'A Framework for Computational Thinking Based on a Systematic Research Review', Baltic J. Modern Computing, 4(3), pp. 583-596.
- Llorens Largo, F., García Peñalvo, F.J., Molero Prieto, X. and Vendrell Vidal, E. (2017) 'La enseñanza de la informática, la programación y el pensamiento computacional en los estudios preuniversitarios', Education in the Knowledge Society (EKS), 18(2), pp. 7-17. https://doi.org/10.14201/eks2017182717
- Lu, J.J. and Fletcher, G.H.L. (2009) 'Thinking about computational thinking', SIGCSE Bulletin Inroads, 41(1), pp. 260-264. https://doi.org/10.1145/1539024.1508959
- Mannila, L., Dagiene, V., Demo, B., Grgurina, N., Mirolo, C., Rolandsson, L. and Settle, A. (2014) 'Computational thinking in K-9 education', ITiCSE-WGR 2014 - Working Group Reports of the 2014 Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education Conference, (June), pp. 1-29. https://doi.org/10.1145/2713609.2713610
- Manso, J. and Monarca, H. (2016) 'Concepciones de la ocde y la unión europea sobre el desarrollo profesional docente', Journal of Supranational Policies of Education, (5), pp. 137-155. https://doi.org/10.15366/jospoe2016.5
- Marin, E.M. (2020) Desarrollo del pensamiento computacional en estudiantes de ingenierías
- para la comprensión óptima de la matemática.
- Maris, S. (2019) 'Pensamiento computacional: por qué incluirlo en el proceso de aprendizaje'. Available at: https://www.net-learning.com.ar/blog/herramientas/pensamiento-computacional-por-que-incluirlo-en-el-proceso-de-aprendizaje.html (Accessed: 20 June 2024).
- Mishra, P., Yadav, A., Henriksen, D., Kereluik, K., Terry, L., Fahnoe, C. and Terry, C. (2013) 'Rethinking Technology & Creativity in the 21st Century', TechTrends, 57(3), pp. 10-14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-013-0655-z
- Motoa, S.S.P. (2019) 'Pensamiento computacional', Revista de Educación y Pensamiento, pp. 107-111.
- Olabe, X.B. and Parco, M.E.O. (2020) 'Integration of computational thinking in compulsory education. Two pedagogical experiences of collaborative learning online', Revista de Educación a Distancia, 20(63). https://doi.org/10.6018/RED.409481
- Ortega, B.R. (2017) Pensamiento computacional y resolución de problemas. Repositorio UAM. Universidad Autónoma de Madrid.
- Papert, S. (1980) Teaching children to be mathematicians vs. teaching about mathematics.
- Papert, S. (1996) 'An Exploration in the Space Of Mathematics education', International Journal of Computers for Mathematical Learning. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00191473
- Pérez-Narváez, H.O. and Roig-Vila, R. (2015) 'Entornos de programación no mediados simbólicamente para el desarrollo del pensamiento computacional. Una experiencia en la formación de profesores de Informática de la Universidad Central del Ecuador', Revista de Educación a Distancia (RED), 46(46).
- Piatti, A., Adorni, G., El-Hamamsy, L., Negrini, L., Assaf, D., Gambardella, L. and Mondada, F. (2022) 'The CT-cube: A framework for the design and the assessment of computational thinking activities', Computers in Human Behavior Reports, 5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chbr.2021.100166
- Polanco, N.P., Ferrer, S.P. and Fernández, M.R. (2021) 'Aproximación a una definición de pensamiento computacional', RIED-Revista Iberoamericana de Educación a Distancia, 24(1), pp. 55-76. https://doi.org/10.5944/ried.24.1.27419
- Raja, T. and Jun, M. (2014) 'Is coding the new literacy?', Mother Jones.
- Repenning, A. and Basawapatna, A. (2017) 'Principles of Computational Thinking', Emerging research, practice, and policy on computational thinking, (April), pp. 291-305. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-52691-1_18
- Riley, D.D. and Hunt, K.A. (2014) Computational thinking for the modern problem solver.
- Roig-Vila, R. and Moreno-Isac, V. (2020) 'El pensamiento computacional en educación. Análisis bibliométrico y temático', Revista de Educación a Distancia (RED), 20(63). https://doi.org/10.6018/red.402621
- Román-González, M., Pérez-González, J.C. and Jiménez-Fernández, C. (2017) 'Which cognitive abilities underlie computational thinking? Criterion validity of the Computational Thinking Test', Computers in Human Behavior, 72, pp. 678-691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.08.047
- Román, M.G. (2016) Codigoalfabetización y pensamiento computacional en Educación Primaria y Secundaria: validación de un instrumento y evaluación de programas.
- Roncoroni, U.O. and Bailón, J. (2020) 'Pensamiento computacional. Alfabetización digital sin computadoras', Icono14, 18(2), pp. 379-405. https://doi.org/10.7195/RI14.V18I2.1570
- School, C. at (2015) 'Computational thinking'. Available at: http://barefootcas.org.uk/barefoot-
- primary-computing-resources/concepts/computational-thinking/ (Accessed: 20 June 2024).
- Segredo, E., Miranda, G. and León, C. (2017) 'Hacia la educación del futuro: El pensamiento computacional como mecanismo de aprendizaje generativo', Education in the Knowledge Society (EKS), 18(2), pp. 33-58. https://doi.org/10.14201/eks2017182335
- Selby, C.C. (2015) 'Relationships: Computational thinking, Pedagogy of programming, and Bloom’s taxonomy', ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, 09-11-Nove, pp. 80-87. https://doi.org/10.1145/2818314.2818315
- Selby, C. and Woollard, J. (2013) Computational thinking: the developing definition. Universidad de Southampton.
- Shute, V.J., Sun, C. and Asbell-Clarke, J. (2017) 'Demystifying computational thinking', Educational Research Review, 22, pp. 142-158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2017.09.003
- Snalune, P. (2015) 'The Benefits of Computational Thinking', (1), pp. 1-27. https://doi.org/10.1093/itnow/bwv111
- Sysło, M.M. and Kwiatkowska, A.B. (2013) 'Informatics for all high school students: A computational thinking approach', Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), 7780 LNCS(February), pp. 43-56. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-36617-8_4
- Tang, X., Yin, Y., Lin, Q., Hadad, R. and Zhai, X. (2020) 'Assessing computational thinking: A systematic review of empirical studies', Computers and Education, 148(December 2019), 103798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103798
- The British Royal Society (2012) 'Shut down or restart?', British Journal of Educational Technology.
- Tsai, M., Liang, J. and Hsu, C. (2021) 'The Computational Thinking Scale for Computer Literacy Education', Journal of Educational Computing Research, 59(4), pp. 579-602. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633120972356
- UNIR, U. I. de la R. (2021) '¿Qué es el pensamiento computacional?', Recuperado de https://www.unir.net/educacion/revista/pensamiento-computacional/ (Accessed: 20 June 2024).
- Valverde-Berrocoso, J., Fernández-Sánchez, M.R. and Garrido-Arroyo, M.C. (2015) 'El pensamiento computacional y las nuevas ecologías del aprendizaje', Revista de Educación a Distancia (RED), (46).
- Wing, J., Cuny, J. and Snyder, L. (2010) 'Research notebook: Computational thinking—What and why?', Recuperado de http://www.cs.cmu.edu/link/research-notebook-computational-thinking-what-and-why (Accessed: 20 June 2024).
- Wing, J.M. (2006) 'Computational thinking', Communications of the ACM, 49(3), pp. 33-35. https://doi.org/10.1145/1118178.1118215
- Yeh, K.C., Xie, Y. and Ke, F. (2011) 'Teaching computational thinking to non-computing majors using spreadsheet functions', Proceedings - Frontiers in Education Conference, FIE, (March 2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/FIE.2011.6142980
- Zapata-Ros, M. (2015) 'Pensamiento computacional: Una nueva alfabetización digital', Revista de Educación a Distancia (RED), 46(46).
- Zapata-Ros, M. (2019) 'Pensamiento computacional desenchufado', Education in the Knowledge Society (EKS), 20(May), p. 29. https://doi.org/10.14201/eks2019_20_a18




