Teaching computational thinking and its effects on children's executive functions
La enseñanza del pensamiento computacional y sus efectos sobre las funciones ejecutivas de los niños

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright statement
The authors exclusively assign to the Universidad EIA, with the power to assign to third parties, all the exploitation rights that derive from the works that are accepted for publication in the Revista EIA, as well as in any product derived from it and, in in particular, those of reproduction, distribution, public communication (including interactive making available) and transformation (including adaptation, modification and, where appropriate, translation), for all types of exploitation (by way of example and not limitation : in paper, electronic, online, computer or audiovisual format, as well as in any other format, even for promotional or advertising purposes and / or for the production of derivative products), for a worldwide territorial scope and for the entire duration of the rights provided for in the current published text of the Intellectual Property Law. This assignment will be made by the authors without the right to any type of remuneration or compensation.
Consequently, the author may not publish or disseminate the works that are selected for publication in the Revista EIA, neither totally nor partially, nor authorize their publication to third parties, without the prior express authorization, requested and granted in writing, from the Univeridad EIA.
Show authors biography
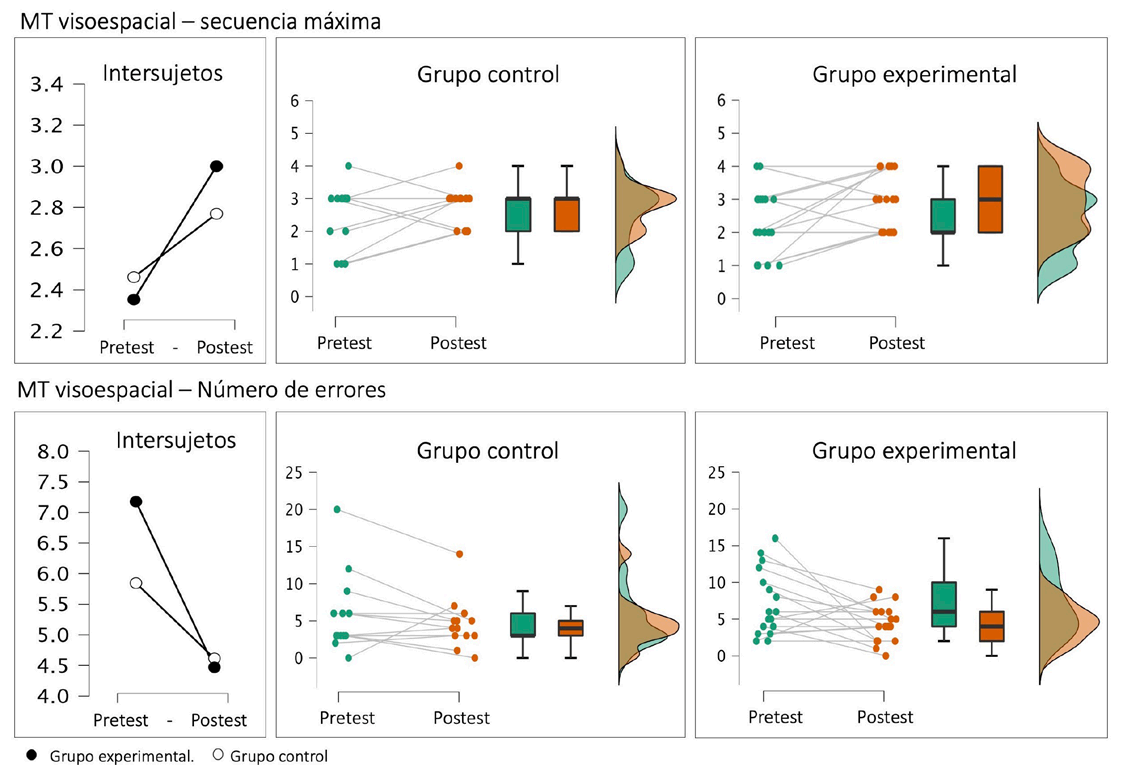
Teaching computational thinking in K-12 education has gained notable prominence in recent years. The main objective of these initiatives is not to teach programming from childhood but to strengthen the ability to reason, solve problems, and develop cognitive processes. For this reason, studying the cognitive effects and impacts that teaching computational thinking has on students has become a field of action with multiple challenges. Seeking to contribute to this new field of study, this pilot test evaluated the effect of a computational thinking training program on the executive functions of school-age children. The results showed that the intervention in computational thinking improved some tasks associated with the executive functions of inhibition, visuospatial working memory, and planning.
Article visits 182 | PDF visits 130
Downloads
- Anderson, P., 2002. Assessment and development of executive function (EF) during childhood. *Child Neuropsychology*, 8(2), pp.71-82. https://doi.org/10.1076/chin.8.2.71.8724.
- Arfé, B. and Vardanega, T., 2019. Imparare a ragionare: il ruolo del pensiero computazionale a scuola. *Giornale Italiano di Psicologia*, 46, pp.765-769. https://doi.org/10.1421/95548.
- Arfé, B., Vardanega, T. and Rononia, L., 2020. The effects of coding on children's planning and inhibition skills. *Computers and Education*, 148, pp.2-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.103807.
- Baddeley, A., Eysenck, M. and Anderson, M., 2009. Memoria de trabajo. In: Memoria, 1st ed. Alianza Editorial, pp.63-91.
- Barkley, R.A., 2011. Executive functioning and self-regulation: Integration, extended phenotype, and clinical implications. New York: Guilford Press.
- Bell, T. and Lodi, M., 2019. Constructing computational thinking without using computers. *Constructivist Foundations*, 14(3), pp.342-351. https://hal.inria.fr/hal-02378761/document.
- Bell, T. and Vahrenhold, J., 2018. CS Unplugged—How is it used, and does it work? In: H.J. Böckenhauer, D. Komm and W. Unger, eds. *Adventures Between Lower Bounds and Higher Altitudes*. Springer, pp.497-521. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98355-4_29.
- Best, J.R. and Miller, P.H., 2010. A developmental perspective on executive function. *Child Development*, 81(6), pp.1641-1660. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2010.01499.x.
- Burke, Q., Byrne, W.I. and Kafai, Y.B., 2016. Computational participation: Understanding coding as an extension of literacy instruction. *Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy*, 59(4), pp.371-375. https://doi.org/10.1002/jaal.496.
- Buss, A.T. and Lowery, K.N., 2020. Inhibitory control and executive function. In: J. Benson, ed. *Encyclopedia of Infant and Early Childhood Development*. 2nd ed. Elsevier, pp.183-193. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809324-5.23669-9.
- Collette, F. and Andres, P., 1999. Lobes frontaux et memoire de travail. In: M. Van der Linden and X. Seron, eds. *Neuropsychologie de lobes frontal*. Francia: Solal, pp.89-114.
- Di Lieto, M.C., Inguaggiato, E., Castro, E., Cecchi, F., Cioni, G., Dell’Omo, M., Laschi, C., Pecini, C., Santerini, G., Sgandurra, G. and Dario, P., 2017. Educational robotics intervention on executive functions in preschool children: A pilot study. *Computers in Human Behavior*, 71, pp.16-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.01.018.
- Di Lieto, M.C., Castro, E., Pecini, C., Inguaggiato, E., Cecchi, F., Dario, P., Cioni, G. and Sgandurra, G., 2020. Empowering executive functions in 5- and 6-year-old typically developing children through educational robotics: An RCT study. *Frontiers in Psychology*, 10(1), p.3084. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.03084.
- Diamond, A., 2012. Executive functions. *Annual Review of Psychology*, 64, pp.135-168. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143750.
- Flores-Lázaro, J.C., Otrosky-Shejet, F. and Lozano-Gutierrez, A., 2014. *Batería neuropsicológica de funciones ejecutivas y lóbulos frontales*. Manual Moderno.
- Gerosa, E., Koleszar, V., Gómez, L., Tejera, G. and Carboni, A., 2021. Cognitive abilities and computational thinking at age 5: Evidence for associations to sequencing and symbolic number comparison. *Computers and Education Open*, 2, p.100043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeo.2021.100043.
- Goldberg, E., 2015. El director ejecutivo del cerebro: Una mirada a los lóbulos frontales. In: *El cerebro ejecutivo*. Editorial Planeta, pp.29-33.
- Golden, C.J., 2020. *STROOP. Test de Colores y Palabras*. Madrid: TEA Ediciones.
- Goldstein, S., Naglieri, J.A., Princiotta, D. and Otero, T.M., 2013. Introduction: A history of executive functioning. In: S. Goldstein and J.A. Naglieri, eds. *Handbook of executive functioning*. Springer, pp.3-12. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-8106-5_1.
- Grover, S. and Pea, R., 2013. Computational thinking in K–12: A review of the state of the field. *Educational Researcher*, 42, pp.38-43. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X12463051.
- Hickmott, D., Prieto-Rodriguez, E. and Holmes, K.A., 2018. Scoping review of studies on computational thinking in K–12 mathematics classrooms. *Digital Experiences in Mathematics Education*, 4, pp.48-69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40751-017-0038-8.
- Kalelioğlu, F., 2015. A new way of teaching programming skills to K-12 students: Code.org. *Computers in Human Behavior*, 52, pp.200-210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.05.047.
- Kay, J., Barg, M., Fekete, A., Greening, T., Hollands, O., Kingston, J. and Crawford, K.A., 2000. Problem-based learning for foundation computer science courses. *Computer Science Education*, 10(2), pp.1-20. https://doi.org/10.1076/0899-3408(200008)10:2;1-C;FT109.
- Kong, S.C., Abelson, H. and Lai, M., 2019. Introduction to computational thinking education. In: S.C. Kong and H. Abelson, eds. *Computational Thinking Education*. Springer, pp.1-10. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-6528-7_1.
- Labusch, A., Eickelmann, B. and Vennemann, M., 2019. Computational thinking processes and their congruence with problem-solving and information processing. In: S.C. Kong and H. Abelson, eds. *Computational Thinking Education*. Springer, pp.65-84. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-6528-7_5.
- Laureys, F., De Waelle, S., Barendse, M.T., Lenoir, M. and Deconinck, F.J.A., 2022. The factor structure of executive function in childhood and adolescence. *Intelligence*, 90, p.101600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2021.101600.
- Liao, Y.K., 2020. A meta-analysis of computer programming on cognitive outcomes: An updated synthesis. In: J. Bourdeau and R. Heller, eds. *Proceedings of ED-MEDIA 2000—World Conference on Educational Multimedia, Hypermedia & Telecommunications*. Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education (AACE), pp.563-569. https://www.learntechlib.org/primary/p/16132/.
- Liao, Y.K. and Bright, G., 1991. Effects of computer programming on cognitive outcomes: A meta-analysis. *Journal of Educational Computing Research*, 7(3), pp.251-266. https://doi.org/10.2190/E53G-HH8K-AJRR-K69M.
- Lozano, I., Roldán, D., Bacelo, A. and Martín, E., 2019. BlueThinking, a programming tool for the development of executive functions at childhood. *Proceedings of the XX International Conference on Human Computer Interaction*, 31. https://doi.org/10.1145/3335595.3335600.
- Miller, D.C. and Halpern, D.F., 2014. Can spatial training improve long-term outcomes for gifted STEM undergraduates? *Learning and Individual Differences*, 32, pp.63-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2014.03.010.
- Miller, G.A. and Cohen, J.D., 2001. An integrative theory of prefrontal cortex function. *Annual Review of Neuroscience*, 24(1), pp.167-202. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.167.
- Moreno, M.M., Otero, T.M. and Ramos, J.G., 2013. Executive functioning in preterm and full-term children: A differential approach. *Child Neuropsychology*, 19(4), pp.392-414. https://doi.org/10.1080/09297049.2012.667071.
- Navarro, J., Calero, M.D. and García-Martín, M.B., 2011. Desarrollo evolutivo de las funciones ejecutivas según la planificación temporal: Influencia del nivel de inteligencia y del nivel socio-familiar. *Psicothema*, 23(1), pp.64-70. https://reunido.uniovi.es/index.php/PST/article/view/8831/8691.
- Navarro, J., Gozález, M., García, C. and Calero, M.D., 2007. Desarrollo de la función ejecutiva según la planificación temporal. *European Journal of Education and Psychology*, 1(3), pp.39-52. https://doi.org/10.30552/ejep.v1i3.25.
- Palladino, P. and Ferrari, M., 2018. Le funzioni esecutive: Differenze evolutive tra fanciullezza e adolescenza. *Psicologia Clinica dello Sviluppo*, 22(1), pp.81-97. https://doi.org/10.1449/86520.
- Papert, S., 1980. *Mindstorms: Children, Computers, and Powerful Ideas*. New York: Basic Books.
- Papert, S., 1993. The children's machine: Rethinking school in the age of the computer. New York: Basic Books.
- Papert, S., 1999. *Mindstorms: Children, Computers, and Powerful Ideas*. 2nd ed. New York: Basic Books.
- Poland, M., 2017. Educational robotics as a learning tool for developing spatial ability in STEM. *International Journal of Technology and Design Education*, 27(1), pp.175-197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-015-9346-5.
- Prensky, M., 2012. From digital natives to digital wisdom: Hopeful essays for 21st century learning. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
- Sáez de Urabain, I.R., Johnson, M.H., Smith, T.J. and Karmiloff-Smith, A., 2014. The importance of action in the development of cognitive and social skills. *Frontiers in Psychology*, 5, p.1361. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01361.
- Schoevers, E.M., Kroesbergen, E.H. and Jolles, J., 2017. The Amsterdam Coding System (ACS): Coding and thinking in 4-8-year-old children. *International Journal of Child-Computer Interaction*, 11, pp.9-19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcci.2016.11.003.
- Shields, G.S., Sazma, M.A., McCullough, A.M. and Yonelinas, A.P., 2016. The effects of acute stress on the memory: A meta-analysis and integration of recent findings. *Psychological Bulletin*, 142(4), pp.337-352. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000030.
- Siegler, R.S., DeLoache, J.S. and Eisenberg, N., 2010. *How children develop*. 3rd ed. Worth Publishers.
- Vatterott, C., 2015. Rethinking homework: Best practices that support diverse needs. Alexandria, VA: ASCD.
- Vassena, R., D'Antone, I. and Castaldi, E., 2018. The role of executive functions in the development of mathematical skills: A literature review. *Psychonomic Bulletin & Review*, 25, pp.64-76. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-017-1306-4.
- Verbruggen, F., McLaren, I.P. and Chambers, C.D., 2014. Banishing the control homunculi in studies of action control and behavior change. *Perspectives on Psychological Science*, 9(5), pp.497-524. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691614526414.
- Wing, J.M., 2006. Computational thinking. *Communications of the ACM*, 49(3), pp.33-35. https://doi.org/10.1145/1118178.1118215.
- Ybarra, M.L., Mitchell, K.J., Finkelhor, D. and Wolak, J., 2007. Internet prevention messages: Targeting the right online behaviors. *Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine*, 161(2), pp.138-145. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.161.2.138.
- Zelazo, P.D., Müller, U., Frye, D. and Marcovitch, S., 2003. The development of executive function. In: W. Riegler, ed. *Handbook of Developmental Psychology*. Blackwell Publishing, pp.345-368.




