Stability of correlations of non-linear electrical activity of the resting brain with closed eyes
Estabilidad de correlaciones de la actividad eléctrica no-lineal del cerebro en reposo con ojos cerrados

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright statement
The authors exclusively assign to the Universidad EIA, with the power to assign to third parties, all the exploitation rights that derive from the works that are accepted for publication in the Revista EIA, as well as in any product derived from it and, in in particular, those of reproduction, distribution, public communication (including interactive making available) and transformation (including adaptation, modification and, where appropriate, translation), for all types of exploitation (by way of example and not limitation : in paper, electronic, online, computer or audiovisual format, as well as in any other format, even for promotional or advertising purposes and / or for the production of derivative products), for a worldwide territorial scope and for the entire duration of the rights provided for in the current published text of the Intellectual Property Law. This assignment will be made by the authors without the right to any type of remuneration or compensation.
Consequently, the author may not publish or disseminate the works that are selected for publication in the Revista EIA, neither totally nor partially, nor authorize their publication to third parties, without the prior express authorization, requested and granted in writing, from the Univeridad EIA.
Show authors biography
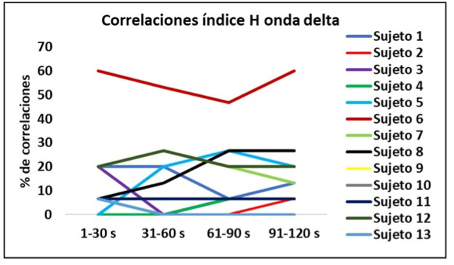
Introduction: the signal of the EEG is usually interpreted from a linear perspective, however, for some decades now the electrical activity of the brain has been studied as a dynamic system, based on the theory of chaos, with non-linear mathematics. Objective: analize the stability of correlations of hurst indices over time in resting subjects with closed eyes. Methods: 13 male university students were evaluated with the brain-interface device Emotiv Epoc® with sampling frequency of 128 Hz. the frequency ranges delta (1-3 Hz), theta (3.5-7 Hz), alpha (8-12 Hz), beta (13-30 Hz) and gamma (>30 Hz) were analyzed. Results: the results show stability in the percentage of correlations in all the bands studied in most of the subjects. this situation occurs in temporary windows of 10, 30 and 60 seconds. Conclusion: this exploratory study shows the persistence intime of non-linear meta-synchronous processes that obey the dynamics of balance chaos/global order of the brain, in resting conditions, basal with closed eyes.
Article visits 459 | PDF visits 267
Downloads
- Bassingthwaighte J, Raymond G. (1994). Evaluating rescaled range analysis for time series. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 2(4): pp. 432-444.
- Bear M, Connors B, Paradiso M. (2016) Neurociencia, la exploración del cerebro. 4° ed. Madrid: Wolters Kluver.
- Buzsaki G. (2006). Rhythms of the brain. London: Oxford University Press.
- Corless M. (2011). Introduction to dynamic systems. Indiana: Purdue University.
- Díaz H, Córdova F, Cañete L, Palominos F, Cifuentes F, Sánchez C, et al. (2015). Order and chaos in the brain: fractal time series analysis of the EEG activity during a cognitive problem solving task. Procedia Computer Science, 55: pp. 1410-1419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.07.135
- Díaz H, Maureira F, Cohen E, Córdova F, Palominos F, Otárola J, et al. (2015). Individual differences in the order/chaos balance of the brain selforganization. Annals of Data Science, 2(3): pp. 1-18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2017.11.378
- Díaz H, Maureira F, Flores G, Fuentes I, García F, Maertens P, et al. (2018). Moving correlations and chaos in the brain during closed eyes basal conditions. Procedia Computer Science, 139: pp. 473-480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.248
- Díaz H, Maureira F, Córdova F. (2018). Times series of closed and open eyes EEG conditions reveal differential characteristics in the temporality of linear and no-linear analysis domain. Procedia Computer Science,139: pp. 570-577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.208
- Díaz H, Maureira F, Flores E, Córdova F. (2018). Intra e inter-hemispheric correlation of the order/chaos fluctuation in the brain activity during a motor imagination task. Procedia Computer Science, 139: pp. 456-463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.250
- Díaz H, Maureira F, Flores E, Cifuentes H, Córdova F. (2019). Synchronizing oscillatory chaos in the brain. Procedia Computer Science, 162: pp. 982-989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.12.076
- Díaz H, Maureira F, Flores E, Gárate E, Muñoz S. (2019). Intra and inter-individual variability in the chaotic component and functional connectivity of the EEG signal in basal closed eyes condition. Procedia Computer Science, 162: pp. 966-973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.12.077
- Díaz H, Maureira F, Otárola J, Rojas R, Alarcón O, Cañete L. (2019). EEG Beta band frequency domain evaluation for assessing stress and anxiety in resting, eyes closed, basal conditions. Procedia Computer Science, 162: pp. 974-981.
- Kumar J, Bhuvaneswari P. (2012). Analysis of electroencephalography (EEG) signals and its categorization-a study. Procedia Engineering, 38: pp. 2525-2536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2012.06.298
- Layek G. (2015). An introduction to dynamical system and chaos. New York: Springer.
- Maureira F. (2017) ¿Qué es la inteligencia? 1° ed. Madrid: Bubok Publishing.
- Maureira F, Flores F. (2018). Electroencefalografía (EEG) y diversas manifestaciones del movimiento: una revisión del 2000 al 2017. EmásF, Revista Digital de Educación Física, 9(51): pp. 48-63.
- Michel C, Murray M. (2012) Towards the utilization of EEG as a brain imaging tool. NeuroImage, ; 61(2): pp. 371-385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.12.039
- Montero F, Moran F. (1992). Biofísica: procesos de auto-organización en biología. Madrid: EUDEMA.
- Pikovsky A, Rosenblum M, Kurths J. (2001). Synchronization: a universal concept in nonlinear sciences. 1° ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Raimundo M, Okamoto J. (2018). Application of Hurst Exponent (H) and the R/S analysis in the classification of FOREX Securities. International Journal of Modeling and Optimization, 8(2): pp. 116-124. https://doi.org/10.7763/ijmo.2018.v8.635
- World Medical Asociation. (2013). World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA, 310(20): pp. 2191-2194.




