Calculation of the diffusion coefficient in liquids by double exposure holographic interferometry: a theoretical study.
Cálculo del coeficiente de difusión en líquidos por interferometría holográfica de doble exposición: estudio teórico

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright statement
The authors exclusively assign to the Universidad EIA, with the power to assign to third parties, all the exploitation rights that derive from the works that are accepted for publication in the Revista EIA, as well as in any product derived from it and, in in particular, those of reproduction, distribution, public communication (including interactive making available) and transformation (including adaptation, modification and, where appropriate, translation), for all types of exploitation (by way of example and not limitation : in paper, electronic, online, computer or audiovisual format, as well as in any other format, even for promotional or advertising purposes and / or for the production of derivative products), for a worldwide territorial scope and for the entire duration of the rights provided for in the current published text of the Intellectual Property Law. This assignment will be made by the authors without the right to any type of remuneration or compensation.
Consequently, the author may not publish or disseminate the works that are selected for publication in the Revista EIA, neither totally nor partially, nor authorize their publication to third parties, without the prior express authorization, requested and granted in writing, from the Univeridad EIA.
Show authors biography
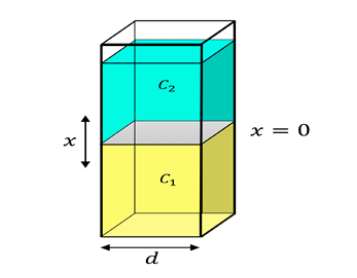
This work is carried out with the purpose of studying theoretically the measurement of the diffusion coefficient (DC) in liquid substances using double exposure holographic interferometry (DEHI). Diffusion has been defined, throughout history, as the phenomenon in which matter moves in a system, from regions with high concentrations to those regions where the concentration is lower, as a consequence of the random movements of its molecules. Diffusion proceeds gradually in the mixture of substances, ending just when the concentrations are equalized; in the case of liquid phase substances, the difusión of a solute in a solvent. For the study of this process, multiple techniques have been used, among which the optical ones stand out, specifically holographic interferometry, which associates the precision of interferometric measurements with the advantages of holography; by implementing IHDE, it is possible to compare the wavefronts, which in principle were separated in time, thus allowing any type of variation in the analyzed object, however small, to be determined by knowing the characteristic wavelength of the light used. In this article, the theoretical development is presented to obtain the mathematical expression from which the CD in liquids can be calculated, using IHDE, highlighting that this is found through the comparison between interferential fringes of the same order recorded at different times, taking into account the distances, measured from the interface between the two liquids, at which they appear. Finally, an analysis of the expression found and how it is applied from experimentally obtained data is carried out.
Article visits 402 | PDF visits 208
Downloads
- Ambrosini, D.; Paloletti, D.; Rashidnia, N. (2008). Overview of Diffusion Measurements by Optical Techniques. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 46(12), pp. 852-864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2008.06.008
- Anderson, J. S.; Saddington, K. (1949). The Use Radioactive Isotopes in the Study of the Diffusion of Ions in Solution. Journal of the American Chemical Society, S381-S386. http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/JR949000S381
- Becsey, J. G.; Maddux, G. E.; Jackson, N. R.; Bierlein, J. A. (1970). Holography and Holographic Interferometry for Thermal Diffusion Studies in Solutions. The Journal Physical Chemistry, 74(6), pp. 1401-1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100701a047
- Bird, R.B.; Stewart, W. E.; Lightfoot, E. N. (1987). Fenómenos de transporte. Un estudio sistemático de los fundamentos del transporte de materia, energía y cantidad de movimiento, México: Ediciones Repla, S.A.
- Bochner, N.; Pipman, J. (1976). A simple method of determining diffusion constants by holographic interferometry. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 9(13), pp. 1825-1831. https://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/9/13/003
- Cadavid, A.; Garzón, J. (2011). Optical Method For Liquid Diffusional Coefficients Calculation. Revista Colombiana de Física, 43(2), pp. 507-512.
- Chhaniwal, V. K.; Anand, A.; Chakrabarty, B. S. (2008). Diffusion studies in transparent liquid mediums utilizing polarization imaging, Opt. Lasers Eng. 46(12), pp. 888–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2008.02.008
- Chhaniwal, V. K.; Anand, A.; Narayanamurthy, C. S. (2005). Diffusion coefficient measurement of transparent liquid solutions using digital holographic interferometry, Optical Measurement Systems for Industrial Inspection IV, Baroda, India: Proc. SPIE 5856, pp. 1109-1113. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.612416
- Chhaniwal, V.; Narayanamurthy, C. S.; Anand, A. (2014). Imaging of mass transfer process using artificial fringe deflection, Opt. Eng. 53(7), 074106. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.OE.53.7.074106
- Crank, J. (1975). The Mathematics of Diffusion, 2ª Edición, Oxford: Oxford Univesity Press.
- Cussler, E.L. (2009). Diffusion Mass Transfer in Fluid Systems, 3ª Edición, Cambridge: Cambridge Univesity Press.
- Fenichel, H.; Frankena, H.; Groen, F. (1984). Experiments on diffusion in liquids using holographic interferometry, American Journal of Physics, 52(8), pp. 735-738. https://doi.org/10.1119/1.13577
- Fernandez, J.L. (1983). La interferometría holográfica como técnica experimental para la determinación de coeficientes de difusión en fase líquida, tesis doctoral, Alicante, Universidad de Alicante, Departamento de Química Técnica.
- Gabelmann-Gray, L.; Fenichel, H. (1979). Holographic Interferomentric Study of Liquid Diffusion, Applied Optics, 18(3), pp. 343-345. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.18.000343
- Ghez, R. (2001). Diffusion Phenomena: Cases and Studies, New York: Kluwer Academic.
- Kreis, T. (2005). Handbook of Holographic Interferometry. Optical and Digital Methods, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. https://doi.org/10.1002/3527604154
- Mialdun, A.; Shevtsova, V. (2011). Measurement of the Soret and diffusion coefficients for benchmark binary mixtures by means of digital interferometry, J. Chem. Phys. 134(4), 044524. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3546036
- Reid, R. C.; Prausnitz, J. M.; Poling, B. E. (1987). The Properties Of Gases & Liquids, 4ª Edición, New York: McGraw-Hill, Inc.
- Riquelme, R.; Lira, I.; Perez, C.; Rayas, J.; Rodríguez, R. (2007). Interferometric measurement of a diffusion coefficient: comparison of two methods and uncertainty análisis, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 40, pp. 2769–2776. http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/40/9/015
- Robinson, R. A.; Stokes, R. H. (2002). Electrolyte Solutions, 2ª Edición, New York: Dover Publications.
- Ruiz, F.; Celdran A.; Santos, C. y Fernández, J. (1985). Liquid Diffusion Measurement by Holographic Interferometry, The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 63(5), pp. 765-771. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.5450630510
- Ruiz, F.; Celdran, A.; Santos, C.; Fernández, J. (1985). Holographic Interferometric Study of Free Diffusion: A New Mathematical Treatment, Applied Optics, 24(10), pp. 1481-1484. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.24.001481
- Shustin, O. A.; Velichkina, T. S.; Chernevich, T. G.; Yakovlev, I. A. (1975). Diffusion Study by a Holographic Method, Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics, 21(1), pp. 24-25.
- Stokes, R. H. (1950). An Improved Diaphragm-cell for Diffusion Studies, and Some Tests of the Method”, Journal of the American Chemical Society, 72(2), pp. 763-767. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01158a032
- Szydlowska, J.; Janowska, B. (1982). Holographic Measurement of Diffusion Coefficients, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 15(8), pp. 1385-1393. https://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/15/8/009




